M.Simons The World's Vintage Sailplanes 1908-45
THE RHOENSPERBERS
With the Rhoensperber, his new design of 1935, Jacobs aimed for a smallish, easily manufactured sailplane for general use, but with a good cross-country performance. The wing was aerodynamically similar to the Bussard, but had a greater span. Some of the increase in span, and hence aspect ratio, was achieved by mounting it at shoulder level on the fuselage instead of high on a pylon. The rigging system was also simplified, the main spars joining inside the fuselage on the centre line but with the main steel pins going in horizontally. All the bending loads were thus carried through the spar. The fuselage was then held to the wing by smaller horizontal pins, one at the drag spar position and the other under the main spar. This last feature necessitated a small underwing 'armpit' fairing, since no access to this pin was possible from inside the fuselage. To retain adequate ground clearance, Jacobs, for the first time, used the 'gull' dihedral form. The tail unit resembled that of the Rhoenbussard but was slightly larger. Two horizontal steel rods, running athwartships, connected the tailplane to the top of the rear fuselage frames.
The most noticeable feature of the Sperber was that the pilot could see in all directions from his 'teardrop'-shaped canopy, which was a light steel tubing frame covered with separate sheets of Plexiglass. The cockpit was large enough for all pilots and there was space for parachute and instruments. The Sperber was also stressed for aerobatics and could be flown safely up to 200 km/h. The improved fuselage and wing root junction, together with the greater span, gave it a better performance than the Rhoenbussard. Flight tests showed that its best glide ratio was close to 22 : 1. This was an excellent figure for a relatively simple club or privately-owned sailplane that could be bought ‘off the shelf'. The type entered production in 1935 at Flugzeugbau Schweyer and about a hundred were produced altogether, before manufacture was discontinued. The first pilot to show what the new aircraft could do was Ludwig Hofmann in 1935. The world record stood at 375 km. It had been set by the great Heini Dittmar almost exactly a year previously in the most refined sailplane of the day, the Fafnir 2. Hofmann followed a similar route but went further into Czechoslovakia, landing at Olesnice after 474 km. It was the first soaring flight over 400 km. Hofmann’s exploit would have been remembered longer if it had not been exceeded within the week. On 29th July four gliders reached Brunn, further still into Czechoslovakia, and the record then stood at 504.2 km. One of the four was a Rhoensperber piloted by Hans Heinemann. There were nine Rhoensperbers competing. The Sperber was not free from teething troubles however. During this Wasserkuppe meeting most of the pilots hurriedly modified their Rhoensperbers by adding spoilers on the upper surfaces of the wings, and on the sixth day all were grounded when a technical analysis indicated an unexpected weakness in the metal root fittings. Flying ceased abruptly while modifications were done, but all soon flew again.
The next year the Rhoensperber was the most popular single type at the Wasserkuppe. Several were exported, one to England where it quickly established a good reputation, especially when flown by Kit Nicholson.
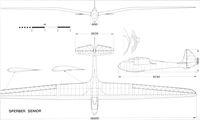
Ernst Udet, a famous sporting pilot who was later to become Goering’s scapegoat for the failure of the Luftwaffe, flew his own personal Rhoensperber at the Berlin Olympic Games display in 1936; like the other sailplanes at this display, the aircraft carried the Olympic linked rings painted on its nose. Udet, as the leader of the German team with Dittmar, Hofmann and Riedel, went to the 1935 Jungfraujoch contest and flew his sailplane there. Ideas were advancing rapidly and the Sperber was already beginning to look out of date. In time for the 1936 Rhoen, Hans Jacobs built for Hofmann an enlarged Rhoensperber, the Sperber Senior. It had greater span and a different wing planform, a larger cockpit and new aerofoils, giving it a better glide ratio at higher speeds. The Sperber Senior was sent to New York by the German Aero Club in June 1937, for Peter Riedel to fly in the Elmira contest. As a training flight, before going to Elmira, Riedel soared for a remarkable seven hours after a launch from Roosevelt Field on Long Island. He flew over downtown Manhattan, crossed to New Jersey on the other side of the Hudson, and back to Roosevelt Field to land. Proceeding to the contest in the following month, Riedel won the most points but as a visitor he was ineligible for the US Championships. After the contest, although attempts were made by American pilots Io buy the Sperber Senior, it was shipped back to Germany and no evidence has been found to show that it ever flew again.
Also flying in the US at this time was a standard Rhoensperber belonging to Emil Lehecka. It carried the name, Guenther Groenhoff.
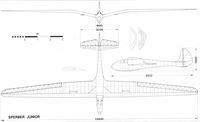
The Rhoensperber was too large for some pilots. Hanna Reitsch needed the seat padded with cushions to bring her head up to the cockpit coaming. For her, Jacobs designed the Sperber Junior. The aerofoil was again the Goettingen 535, but the span was stretched and the planform was similar to Hofmann’s aircraft. The fuselage was tailored to fit Hanna's small figure, the ‘teardrop' cockpit canopy being dispensed with and instead a wooden hood with partly glazed portholes was substituted, and a shape rather like that on the Fafnir 1, was used. Hanna’s aircraft was painted with a spectacular blue and cream ‘sunburst' color scheme. Today several Rhoensperbers survive in varying conditions. Two are complete in storage in Germany, but are not airworthy. Another, Nicholson’s old aircraft, was rebuilt during the late 'seventies at Tangmere, although fitted with a Rhoenbussard tailplane and elevator.
The performance figures, weights, etc, quoted below come from the DFS flight tests reported by Spilger in 1937.
Technical data:
Rhoensperber: Span. 15.20 m. Wing area. 15.1 sq m. Aspect ratio: 15.3. Empty weight. 182.5 kg. Flying weight. 287.5 kg. Wing loading. 19.0 kg/sq m. Aerofoil, Goettingen 535 at root and over centre section, tapering to thin symmetrical Goettingen 409 at the tip. Best glide ratio, 1:21.6 at 63 km/h. Minimum sinking speed. 0.73 m/sec at 50.5 km/h. Sink at 100 km/h, 1.74 m/sec.
Sperber Senior: Span, 16.00 m. Wing area, 16.2 sq m. Aspect ratio, 15.8. Empty weight, 186 kg. Flying weight, 291 kg. Wing loading, 18.0 kg/sq m. Aerofoil, Goettingen 757 at root and centre section, tapering to Goettingen 767 at tip. Best glide ratio, 1:22.7 at 67 km/h. Minimum sinking speed 0.74 m/sec at 56.5 km/h. Sink at 100 km/h, 1.63 m/sec.
Sperber Junior: Span. 15.60 m. Wing area, 15.5 sq m. Aspect ratio. 15.7. Empty weight, 175 kg. Flying weight, 280 kg. Wing loading, 18.1 kg/sq m. Aerofoils, as for Rhoensperber. Best glide ratio, 1:24.3 at 68 km/h. Minimum sinking speed 0.65 m/sec at 48.5 km/h. Sink at 100 km/h, 1.5 m/sec.
Описание:
- M.Simons The World's Vintage Sailplanes 1908-45
- M.Hardy. Gliders & Sailplanes of the world
Фотографии
-
GL / M.Simons - The World's Vintage Sailplanes 1908-45 /Kookaburra/
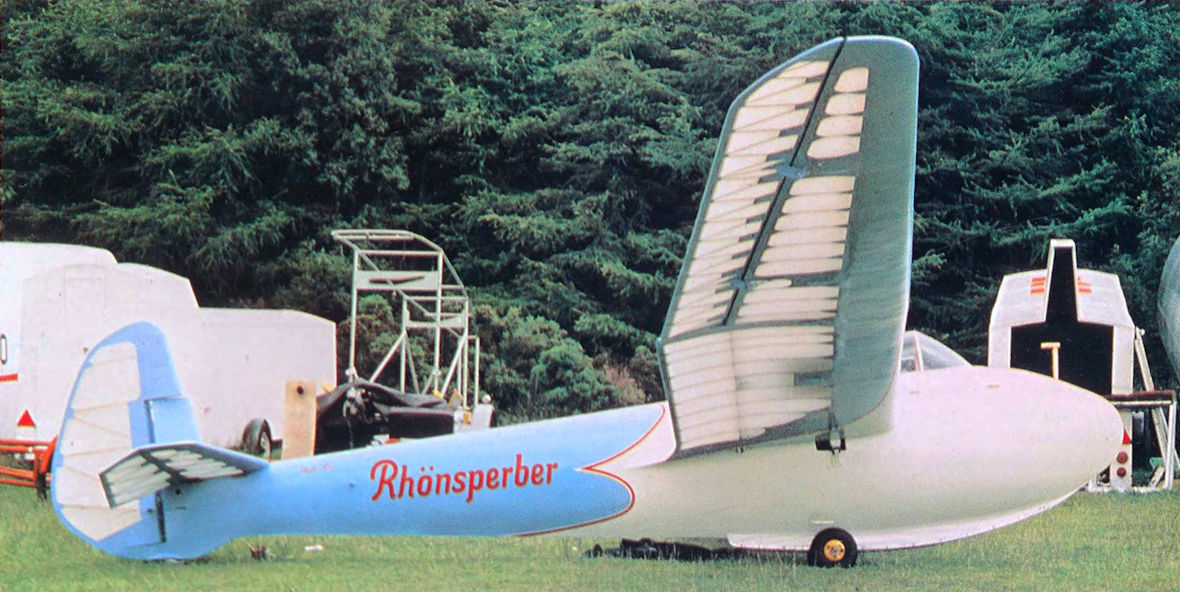
View of the rebuilt Rhoensperber, the only one airworthy at the time of publication. The tailplane is from a Rhoenbussard and one wing had to be built entirely from scratch. The color scheme has been restored as closely as possible to that of the aircraft as it was in 1939. The work of rebuilding was done at Tangmere by Fred Stickland and Rodi Morgan.
-
GL / M.Simons - The World's Vintage Sailplanes 1908-45 /Kookaburra/
The Rhoensperber at Dunstable in 1938 at the British National Championships. Earlier it had a German factory color scheme of similar style but in different hues. It was repainted in red, white and blue before this photograph was taken. After lying idle and rotting for more than thirty years and losing parts, it was restored to fly again in 1980.
-
GL 1982- / M.Hardy - Gliders and Sailplanes /Gliders & Sailplanes of the world/ (1)
Schweyer Rhonsperber.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1991-09 / M.Challinor - 60 years of Ups on the Downs
Kit Nicholson’s Rhonsperber, still seen at Dunstable today but without the attendant plus-fours.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1986-11 / A.Welch - Vintage gliders galore
Регистрационный номер: BGA260 More conventional and elegant was Schleicher Rhonsperber BGA 260, seen with Manuel Condor BGA 2161 behind it.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Manuel Condor - Великобритания - 1976
-
Flight 1937-08 / Flight
Mr. Nicholson took advantage of the wind to show some of the capabilities of his Rhonsperber glider.
-
GL / M.Simons - The World's Vintage Sailplanes 1908-45 /Kookaburra/
Heinemann's Rhoensperber at the start of the record-breaking 504 km flight in 1935. The sailplane was named Nobel II, the name appearing under both wings as well as on the fuselage sides, with the usual D for Deutschland. The contest number on the rudder was 10.
-
Flight 1938-07 / Flight
Maj. Alan Goodfellow, Sir Francis McClean, and Mr. J. R. Ashwell-Cooke - all pioneer sponsors of gliding in this country - with Dr. Dewsbury in the Rhonsperber.
-
Flight 1936-05 / Flight
The Bucker Jungmann two-seater trainer, and above it the Rhonsperber sailplane.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Bucker Bu.131 Jungmann - Германия - 1934
-
GL / M.Simons - The World's Vintage Sailplanes 1908-45 /Kookaburra/
Регистрационный номер: D4-502 Peter Riedel flying the Sperber Senior over New York in 1937. The registration was slightly unusual since the dash following the letter D had been omitted. The Olympic rings appeared on the fuselage below the cockpit coaming, indicating that the aircraft participated in the 1936 Berlin displays.
-
Авиация и Время 2003-06 / В.Виноградов, Е.Биске - Неповторимая Ханна Райч
Ханна Райч возле планера "Юниор", на котором летала в Альпах
-
GL / M.Simons - The World's Vintage Sailplanes 1908-45 /Kookaburra/
More photographs of what was undoubtedly one of the most elegant and refined sailplanes of its time. Note the superb finish. The smart sunray paint scheme was in medium blue on a cream background. Even for the diminutive Hanna Reitsch, for whom the sailplane was specially designed and built, there was no room to spare.
-
GL / M.Simons - The World's Vintage Sailplanes 1908-45 /Kookaburra/
The Sperber Junior in flight.
- Фотографии