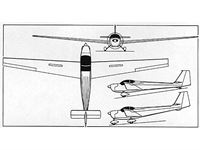
Описание
Страна : Германия
Год : 1963
Планер
Two-seat powered sailplane, particularly suitable for basic and advanced training
Варианты
- Akaflieg Munchen - Mu.13 - 1935 - Германия
- Scheibe - Bergfalke - 1951 - Германия
- Scheibe - SF-25 Motorfalke - 1963 - Германия
M.Hardy. Gliders & Sailplanes of the world
Scheibe SF-25C and C-S Falke '76 (Falcon) FGR
Following the successful development of the SF-24 Motorspatz powered glider from the L-Spatz-55 and L-Spatz-lll single-seater sailplanes, it was a logical step to produce a two-seater motor glider based on the popular Bergfalke III. This emerged as the SF-25 Motorfalke which, in its original form, had a cantilever high-set wooden wing with Schempp-Hirth air brakes similar to that of the Bergfalke III but, unlike the sailplane, was a side-by-side rather than a tandem two-seater. Powerplant was a 28hp Hirth-built Solo 'flat four' air-cooled two-stroke engine in an installation very similar to the SF-24B Motorspatz, and with a fuel tank of 5.5 Imp gallons capacity. The fuselage aft of the cockpit was very similar to the Bergfalke Ill's, being the traditional Scheibe fabric-covered welded steel tube structure, and the wooden tail unit and fixed monowheel landing gear were also similar to the Bergfalke's. The two pilots have dual controls as standard and the Motorfalke went into production, a total of 25 having been built by early 1966. Later versions of the SF-25, now known simply as the Falke (or Falcon), had low-set two-piece cantilever wooden wings developed from the Motorfalke's with air brakes in the upper surfaces and slight forward sweep; the SF-25B's span was now 50ft 2 1/2in and aspect ratio 13.4, compared with the Motorfalke's 54ft 5 1/2 in span and aspect ratio of 16. A more powerful engine was fitted, the forward fuselage underside fairing for the fixed monowheel with brake was revised in shape and outrigger stabilising wheels were fitted under each wing, so that the SF-25B was almost a different aeroplane to the Motorfalke, although just as suitable for basic and advanced training. Its powerplant was a 45hp Stamo MS 1500-1 modified Volkswagen 'flat four' engine which also incorporated some Porsche parts; this was started on the ground or in the air by a pull-cable starter in the cabin, with an electrical starter available as an optional extra and the fuel capacity was 8.5 Imp gallons. Another optional extra for the SF-25B is a tow-hitch for winch-launching. The tail unit is of wooden construction and there is a steerable tailwheel; dual controls are standard.
The SF-25C is an improved version of the SF-25B, differing from it primarily in having a 65hp Limbach SL 1700EA modified Volkswagen 'flat four' engine driving a two-blade propeller; an electric starter is fitted and the single fuselage fuel tank has a capacity of 9.9 Imp gallons, or 12.1 Imp gallons optionally. The SF-25C received its type certification in September 1972 and by January 1980 a total of 295 of this version had been built by Scheibe, plus another 50 built under licence by Sportavia in Germany, who also built 80 SF-25Bs. About 200 SF-25Bs had been built by Scheibe, about 10 more by Aeronautica Umbra Sppp in Italy, plus 35 by Vickers-Slingsby, who are producing a modified version of the B as the T61E Venture T Mk 2 for the Air Training Corps. The SF-25C-S is a further improved variant with a Hoffman feathering propeller, adjustable engine cowl flap and slightly modified fuselage, and 20 of this version had been built by January 1980. Further optional features include an additional exhaust outlet and a slower-turning propeller, these reducing the noise level to less than 60 dB. Optional wing folding is also available, reducing the span to 31ft 2in for easier hangar storage. The Falke '76 was an improved model and featured a number of design improvements, including a domed cockpit canopy, an enlarged fin and smaller rudder with greater sweepback, a coating of laminated glassfibre for the forward section of the fuselage, some engine and exhaust modifications and an alternative twin-wheel main landing gear with wheel spats, which is offered as an option to customers. The non-retractable monowheel is normally unsprung, but a rubber-sprung monowheel is also offered as optional. Current production version is the C-Falke '80, which becomes the SF-25K K-Falke '80 with fully-folding wings. Latest version of the SF-25C has an 80hp Limbach L2000 'flat four' engine.
Data: SF-25C and C-S Falke '76
Span: 50 ft 0 1/4 in
Length: 24 ft 9 1/4 in
Height: 6 ft 0 3/4 in
Wing area: 195.9 sqft
Aspect ratio: 13.8
Empty weight: 826 lb
Max weight: 1,345 lb
Max speed: 112 mph (power on)
Max cruising speed: 99 mph
Min sinking speed: 3.28 ft/sec at 43.5 mph
Best glide ratio: 23:1
Take-off run: 590 ft
Range with max fuel: 466 miles
Scheibe SF-25E Super-Falke
The Super-Falke is basically an SF-25C-S with a wing increased in span to 18m (59ft 0 3/4 in); the fuselage aft of the wing has a wider section than that of the C-S to improve airflow at the wing root, and the fairing for the non-retractable monowheel, which is now rubber-sprung as standard, is now larger. Production aircraft also have a tailwheel, Schempp-Hirth air brakes in the wing upper surfaces and a cabin heater fitted as standard. The same 65hp Limbach SL 1700EA engine as in the SF-25C is fitted, driving a two-blade feathering propeller; there is a 12 volt battery and alernator for electrical engine starting, and the engine cowl flap is adjustable. Wing folding of the outer panels is optional, as on the SF-25C-S, and the same outrigger stabilising wheels are fitted under each wing. The Super-Falke made its first flight in June 1974, and the type took first place in the advanced two-seater class at the First International Motor Glider Competition; a total of 52 Super-Falkes had been delivered by January 1980. The type is structurally the same as the SF-25C-S, and has the same side-by-side seating with dual controls; like the SF-25C, optional folding wings are available for easier hangar stowage.
Span: 59 ft 0 3/4 in
Length : 24 ft 11 3/4 in
Height: 6 ft 0 3/4 in
Wing area: 187.3 sqft
Aspect ratio: 17.8
Empty weight: 904 lb
Max weight: 1,389 lb
Max speed: 112 mph
Max cruising speed: 99 mph
Min sinking speed: 2.79 ft/sec at 47 mph
Best glide ratio: 29:1 at 53 mph
Take-off run: 490-655 ft
Endurance: 4 hours
Scheibe SF-28A Tandem-Falke FGR
The Tandem-Falke, as its name implies, is a development of the SF-25C Falke wth the two seats in tandem positioned over the wings under a lengthened one-piece perspex canopy, instead of the side-by-side layout of the earlier Falke series. The Tandem-Falke can be flown solo from the front seat, with space for up to 198lb of baggage on the rear seat. Design work on the SF-28 began in 1970 and the prototype, registered D-KAFJ, made its first flight in May 1971, powered by a 45hp Stamo MS 1500 modified Volkswagen engine. The production SF-28A has a 65hp Limbach SI 1900EA1 engine, the same as fitted to the SF-25C Falke but fitted to drive a Hoffman two-blade variable-pitch feathering propeller; a fixed-pitch prop is available as an option and the fuel capacity totals 8.8 Imp gallons. Altogether 112 Tandem-Falkes had been built by January 1980 and the Tandem-Falke has competed in the German Motor Glider Competition; one flown by Peter Ross set up two United Kingdom records for motor gliders in 1976. The type has the same basic wooden construction with fabric-covered welded steel tube fuselage as the SF-25 Falke series; both wing span and length are slightly greater than the SF-25C's, the fin and rudder are now unswept. The single-spar wooden wings have spoilers in the upper surfaces and no flaps; there is an outrigger stabilising wheel on a nylon leg under each wing, as well as a faired non-retractable monowheel with internal brake and a steerable tailwheel. There is a trim tab in the elevator.
Span: 53 ft 5 3/4 in
Length: 27 ft 3 in
Height: 5 ft 1 in
Wing area: 197.0 sq ft
Aspect ratio: 14.5
Empty weight: 881 lb
Max weight: 1,345 lb
Max speed: 118 mph (in smooth air, power off)
Max cruising speed: 87 mph
Min sinking speed: 2.95 ft/sec at 43.5 mph
Best glide ratio: 27:1 at 53 mph
Take-off run: 575 ft
Range with max fuel: 261 miles
Scheibe SF-33
This single-seater motor glider was developed from the earlier SF-29 and is intended especially for training and powered cross-country flying, and for use by clubs as well as private owners. It made its first flight in 1977, and although it did not go into production it was aimed at filling the gap between the two-seater SF-25 Falke variants and the higher performance single-seat powered gliders such as the PIK-20E and Nimbus 2M; it was also designed for ease of handling by the less experienced pilot. Like the earlier SF-25 Falke variants which it resembles, the SF-33 is a cantilever low-wing monoplane of basically wooden construction; the fuselage is a steel tube framework covered with plywood and fabric, and the engine cowling panels are of glassfibre reinforced plastic. The two-piece wings have plywood leading edges and wooden ailerons, and there are spoilers in the wing upper surfaces. The wooden tail unit has a trim tab in the starboard elevator. The landing gear consists of a fixed monowheel, a steerable tailwheel linked to the rudder for taxying, and two detachable outrigger wheels under the wings. The pilot sits under a large blown canopy that opens sideways to starboard and gives excellent all-round visibility. Powerplant is a 900cc BMW two-cylinder motorcycle engine derated to 35hp and driving a Hoffman two-blade variable-pitch propeller; total fuel capacity is 4.8 Imp gallons. The SF-33 is self-launching, and its gliding performance is claimed to be comparable to that of the popular Schleicher Ka 8.
Span: 49 ft 2 1/2 in
Length: 22 ft 1 3/4 in
Height: 4 ft 9 in
Wing area: 134.5 sqft
Aspect ratio: 18.0
Empty weight: 661 Ib
Max weight: 904 lb
Max speed: 106 mph (in smooth air, power off)
Max cruising speed: 93 mph (power on)
Min sinking speed: 2.79 ft/sec at 50 mph
Best glide ratio: 29:1 at 47 mph
Take-off run : 490-655 ft
Range with max fuel: 186 miles
Vickers-Slingsby T 61E Venture
Slingsby Sailplanes - now Slingsby Engineering Ltd (Aircraft Division) began production under licence of the Scheibe SF-25B Falke two-seat motor glider as the T61, construction of the first Slingsby-built example beginning in April 1970; a total of 35 were built. The T61 and T61A have the 45hp Stamo MS1500-1 engine with manual starter as fitted to the SF-25B, whereas the T61C has the Stamo MS1500-2 with electric starter. With the firm's long record of supplying gliders for the needs of the Air Training Corps, it was not surprising that the possibilities of a motor glider such as the T61 for ATC training should be considered, especially its time-saving potential in being able to dispense with winch launches and retrieving vehicles, and its ability to continue flying in weather when unpowered sailplanes were grounded. A prototype Slingsby-built T61 serialled XW983 was evaluated as the Venture T Mk 1, and this led to an order for 15 of a special version, the Venture T Mk 2, by the Ministry of Defence (Air) for Air Training Corps use. The first production T Mk 2, serialled XZ550, made its first flight on 2 July 1977 and deliveries began that autumn. A total of 19 T61F Venture T Mk 2s had been completed by the beginning of 1980. The T Mk2 differs from previous Slingsby- and Scheibe-built SF-25Bs in having a special glassfibre spar encased in plywood and many other glassfibre components are employed. Use of this material in the spars and elsewhere both reduces the empty weight and increases the maximum permissible take-off weight, and hence payload. New glassfibre seats are also featured of improved comfort and designed to reduce the hazard of loose articles slipping under the seat into the control area. The powerplant is a 45hp Rollason Ardem 'flat four' of 1,600cc driving a two-blade fixed-pitch propeller; this is a version of the Volkswagen car engine modified by Rollason Aircraft and Engines Ltd of Shoreham, Sussex, and has single ignition and an electric starter.
The T61G Falke is a civil development of the Venture T Mk 2, with a 60hp Limbach SL 1700EA 'flat four' engine driving a Hoffman two-blade fixed-pitch propeller (a variable-pitch one can be fitted if desired).
Data: Venture TMk 2
Span: 50 ft 0 1/4 in
Length: 24 ft 9 1/4 in
Height: 6 ft 0 3/4 in
Wing area: 195.9 sqft
Aspect ratio: 13.8
Empty weight: 827 lb
Max weight: 1,350 lb
Max level speed: 92 mph
Min sinking speed: 3.28 ft/sec
Best glide ratio: 22:1
Take-off run: 650 ft
Range: 248 miles
- M.Hardy. Gliders & Sailplanes of the world
Фотографии
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1966 / 05 - Sailplanes
Scheibe Motorfalke powered sailplane (28 hp Solo engine)
-
GL 1982- / M.Hardy - Motor Gliders /Gliders & Sailplanes of the world/ (2)
Scheibe SF-25B Motorfalke.
-
Air-Britain Archive 1983-03
Регистрационный номер: OO-MVB Scheibe SF.25B Motorfalke OO-MVB (1925) was one of two delivered in 1969 to the national gliding centre.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1972 / 03 - Sailplanes
Scheibe SF-25B Falke powered sailplane (45 hp Stamo MS 1500 engine)
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 2000 / 2-01 - AIRCRAFT - FIXED-WING - CIVIL
Регистрационный номер: D-KMRH Scheibe SF 25C Rotax Falke with optional tricycle landing gear (1994)
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1975 / 03 - Sailplanes
SF-25C-S Falke, developed from the SF-25B with redesigned fuselage, engine cowl flap and feathering propeller
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1976 / 03 - Sailplanes
Scheibe SF-25B (SF-25C-S ???) Falke side-by-side two-seat powered sailplane
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1976 / 03 - Sailplanes
Scheibe SF-25E Super-Falke motor glider, with increased wing span
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-04 / News Spotlight
Following trials Boscombe Down, the Vickers-Slingsby T61E Venture T Mk 2 motor glider has now entered service with the Air Training Corps.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1977-09 / News Spotlight
Регистрационный номер: XZ550 The Air Training Corps is to re-equip with 15 Vickers-Slingsby T61E Venture Mark 2 self-launched gliders.
First Vickers-Slingsby T61E Venture Mk.2 for the Air Cadets, XZ550 was exhibited at R.A.F. Finningley during the Queen's Silver Jubilee Review of the R A.F. on 29th July 1977 -
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1974 / 03 - Sailplanes
Регистрационный номер: G-AYPY Slingsby T.61, licence-built version of the Scheibe SF-25B powered sailplane
-
GL 1982- / M.Hardy - Motor Gliders /Gliders & Sailplanes of the world/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: G-BDGX Scheibe SF-25E Super-Falke.
-
Air Pictorial 1977-06
Регистрационный номер: G-BEGG The R.A.F.G.S.A.’s Superfalke G-BEGG at Finmere 6/3/77;
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1976 / 03 - Sailplanes
Регистрационный номер: G-BARZ British-registered Scheibe SF-28 Tandem-Falke powered sailplane
-
GL 1982- / M.Hardy - Motor Gliders /Gliders & Sailplanes of the world/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: G-BBGA Scheibe SF-28A Tandem-Falke.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1975 / 03 - Sailplanes
Scheibe SF-28 Tandem-Falke two-seat powered sailplane (60 hp Limbach SL 1700 EA 1 engine)
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1976 / 03 - Sailplanes
Modified propeller and exhaust silencer fitted to SF-25C
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1975 / 03 - Sailplanes
Scheibe SF-29 single-seat powered sailplane
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 2000 / 2-01 - AIRCRAFT - FIXED-WING - CIVIL
Scheibe SF 25C Falke powered by Rotax 912 A engine, with second side view (lower) of Rotax-powered Falke with nosewheel landing gear (1994)
- Фотографии