Варианты
- Akaflieg Munchen - Mu.13 - 1935 - Германия
- Scheibe - Bergfalke - 1951 - Германия
- Scheibe - SF-25 Motorfalke - 1963 - Германия
M.Hardy. Gliders & Sailplanes of the world
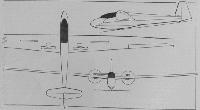
Scheibe Bergfalke IV
This tandem two-seater training and competition sailplane had its origins in the prototype Mu-13E Bergfalke I general purpose two-seater designed and built by Dipl-Ing Egon Scheibe in Austria, and which made its first flight on 5 August 1951. At the end of that year the Scheibe Flugzeugbau GmbH was founded and the Bergfalke (or Mountain Falcon) was the first type to go into production at the new company's works at Munich-Riem airport. From the Mu-13E the Bergfalke II was developed with 4° forward sweep on the wings, and more than 250 of these two versions were built; the Mk II was succeeded by the Bergfalke II/55 two-seater which also had a fabric-covered steel tube fuselage and single-spar wooden wings of 54ft 6in span and 15.6 aspect ratio, these being of 14.5% Mu section. The II/55 was succeeded by the Bergfalke III with a more streamlined cockpit canopy, a redesigned and taller fin and rudder and 2° forward sweep on the wings of the same section, which have Schempp-Hirth air brakes; the monowheel is non-retractable as before, but a tailwheel replaces the ll/55's tailskid. A few Bergfalke Ills were built under licence by the Spanish firm Stark Iberica SA. The Mk III was succeeded in its turn by the Bergfalke IV which has a new wing of Wortmann section and 2ft greater span, with an aspect ratio of 17.4; this gives improved performance, including a best glide ratio of 34:1 instead of 28:1 and a lower minimum sinking speed. Construction of the prototype Bergfalke IV began early in 1969 and the first flight was made a few months later, and a total of 70 of this version had been built by the beginning of 1978. The cantilever mid-wings are of all-wood construction with a fabric-covered plywood skin; they have single laminated beechwood box spars joined at the fuselage centreline with a single vertical pin. The ailerons and Schempp-Hirth air brakes are also of wood. Like previous versions, the welded steel tube fuselage is fabric-covered, the nose section on the Mk IV being a moulded glassfibre shell. The tail unit is of wooden construction, the tailplane being mounted on the fuselage forward of the fin; there is a Flettner trim tab in the starboard elevator. The landing gear consists of a non-retractable monowheel and a tailwheel. The two pilots are seated under a blown Plexiglas canopy.
A Bergfalke IV has been modified by the Flying Training School of the Detmold Aero Club into a motor glider, with one Lloyd LS-400 piston engine in the fuselage driving a pair of small two-bladed pusher propellers which rotate within cutouts in each wing near the trailing edge; there is a 12v battery for engine starting. In this form the Bergfalke IV is known as the LVD BF IV-BIMO, the letters LVD signifying Schulerfluggemeinschaft der Luftsportverein Detmold EV. Scheibe themselves were test flying another powered version of the Bergfalke IV early in 1976 with a 52hp Hirth O-28 'flat twin' engine mounted on a retractable pylon aft of the cockpit and driving a two-blade fixed-pitch tractor airscrew; the engine can be raised and lowered into the fuselage electrically in less than 20 seconds, retracting behind closed doors. This version was known as the Bergfalke IVM.
Data: Bergfalke IV
Span : 56 ft 5 1/4 in
Length: 26 ft 3 in
Height: 4 ft 11 in
Wing area: 183 sqft
Aspect ratio: 17.4
Empty weight: 661 Ib
Max weight: 1,102 lb
Max speed: 124 mph (in smooth air)
Max aero-tow speed: 87 mph
Min sinking speed: 2.23 ft/sec at 47 mph
Best glide ratio: 34:1 at 59 mph
- M.Hardy. Gliders & Sailplanes of the world
Фотографии
-
GL 1982- / M.Hardy - Gliders and Sailplanes /Gliders & Sailplanes of the world/ (1)
Регистрационный номер: OE-0295 Scheibe Bergfalke.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1964 / 03 - Sailplanes
Scheibe Bergfalke-II/55 two-seat general-purpose sailplane
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1966 / 05 - Sailplanes
Scheibe Bergfalke-III two-seat general-purpose sailplane
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1976 / 03 - Sailplanes
Scheibe Bergfalke-IV two-seat training and competition sailplane
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1972 / 03 - Sailplanes
Scheibe Bergfalke-IV two-seat training and competition sailplane
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1976 / 03 - Sailplanes
Scheibe Bergfalke-IV fitted with two Lloyd engines by the Detmold Aero Club Flying Training School
- Фотографии