Фотографии
-
Starting in the 1950s Canadair carried out extensive studies into V/STOL design, including the convertiplane concept. The CL-74 army reconnaissance project powered by two Allison T63-A-3 turboprop engines was not built but the CL-84 produced in 1964 did put much of the research to good use.
Самолёты на фотографии: Canadair CL-84 Dynavert - Канада - 1965
-
Artist’s impression of an attack version of the CL-84.
Самолёты на фотографии: Canadair CL-84 Dynavert - Канада - 1965
-
Responding to an American Airlines’ request for proposals, Canadair developed the CL-246 study for a 48-passenger STOL airliner powered by four Lycoming T53-19A turboprop engines.
Самолёты на фотографии: Canadair CL-246 - Канада - 1972
-
The CL-60 was to have become the T-36 navigation trainer/transport designed for the USAF and produced jointly with Beechcraft but it became the victim of defence cuts and was judged to be too complex to be adapted for civil certification as the CL-42.
Самолёты на фотографии: Canadair CL-42 / CL-60 - Канада - 1952
-
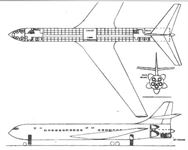
The proposed CL-50A jet airliner which pre-dated both the Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8, was one of several studies carried out under this designation in 1951. Several jet and turboprop engine configurations were considered including the unusual cluster of five jet engines illustrated.
Самолёты на фотографии: Canadair CL-50 - Канада - 1955
-
The attempt to supply the USAF with a crew readiness trainer in the shape of the CL-53 was no more successful than the earlier CL-42/CL-60. Similar in layout to other executive aircraft in this class, the CL-53 did not progress as a bizjet either, although it was one of the first to be proposed as a trijet.
Самолёты на фотографии: Canadair CL-53 - Канада - 1956
-
The CL-69 was the designation given to a series of studies into a basic design which could have applications in the corporate, utility and cargo markets.
Самолёты на фотографии: Canadair CL-69 - Канада - 1958
-
Unlike the studies for the CL-202 carried out in 1962, the CL-203 of the same year was a totally in-house design which would have been powered by two Rolls-Royce Spey engines.
Самолёты на фотографии: Canadair CL-202 / CL-203 - Канада - 1962
-
Intended to be a heavy transport aircraft in the same category as the Lockheed C-5A, the CL-99 powered by four P&W JT3D-14 turbofans was proposed to the RCAF in 1961.
Самолёты на фотографии: Canadair CL-202 / CL-203 - Канада - 1962
-
One of several studies for a military tactical transport, the CL-202 was based on the Handley Page Herald.
Самолёты на фотографии: Canadair CL-202 / CL-203 - Канада - 1962
-
An early study for a water bomber carried out in 1962, the CL-204 bears a close resemblance to the CL-43 bush transport study of some eight years earlier.
Самолёты на фотографии: Canadair CL-204 - Канада - 1962
Статьи
- Round-Out
- A.Pelletier - Paper Darts to Deltas
- A.Thomas - More from Mesopotamia
- A.Walg - Wings over the Steppes (3)
- B.Elliott - Bears in the Air
- B.Marshall - The 'Flea' and Me
- B.van der Klaauw - Fokker's American Heydays
- B.Walters - Nearly, but not Quite
- D.Henley - Singular Customer
- K.Wixey - Corpulent Feline (1)
- K.Wixey - 'Wild Catfish'
- M.Davey - Pacific Naval War
- M.Lopes - In at the Deep End