Northrop Alpha и Beta
В 1928 году Джон К. Нортроп и Кен Джей основали в Бербанке, штат Калифорния, компанию "Avion Corporation". Годом ранее Нортроп спроектировал первый самолет компании "Lockheed", названный Vega. Первым проектом Нортропа для новой компании стал самолет, названный "Flying Wing" ("Летающее крыло"), Однако более интересным был другой проект - Alpha, представлявший собой цельнометаллический одномоторный низкоплан, рассчитанный на перевозку семи человек. В 1929 году компания "Avion Corporation" была переименована в "Northrop Aircraft Corporation" и стала подразделением корпорации "United Aircraft and Transport Corporation", в которую также входила компания "Boeing". Авиакомпания "Trans Continental and Western Air Inc." заказала пять самолетов Alpha, оснащенных двигателями Pratt & Whitney Wasp мощностью 420 л.с, и приступила к их эксплуатации 20 апреля 1931 года на маршруте Сан-Франциско - Нью-Йорк с 13-ю промежуточными посадками (перелет занимал чуть более 23 часов). В целях обеспечения возможности полетов в сложных метеоусловиях и ночью самолеты Alpha были оснащены современным радионавигационным оборудованием, а для полетов в зимнее время они первыми из коммерческих авиалайнеров стали оснащаться пневматической противообледенительной системой Goodrich на крыле и передних кромках хвостового оперения. 13 из 17 самолетов Alpha поступили в авиакомпанию TWA, а три - переданы для испытаний в авиакорпус Армии США, где в случае поступления серийных машин они бы получили обозначение C-19.
Разные модификации самолета получили обозначения Alpha 2, Alpha 3, Alpha 4 и Alpha 4-A, на некоторых из них вносились отдельные изменения. Изменения, опробованные на последних машинах, переносились затем на более ранние самолеты, включая установку обтекателей на стойках шасси. Последней модификацией стал грузовой самолет Alpha 4-A, способный перевозить 567 кг груза и оснащенный, как и модификация Alpha 4, двигателями Wasp мощностью 450 л.с. Большая часть более ранних машин была затем ремоторизирована данными двигателями. Последний оставшийся Alpha был выкуплен TWA в 1975 году и после восстановления передан в Национальный музей авиации и космонавтики Смитсонианского института.
<...>
Описание:
- Northrop Alpha и Beta
- Flight, September 1931
MORE SPEED
Фотографии
-
Flight 1931-09 / Flight
The clean lines of the Alpha show well in this three-quarter front view.
-
Aviation Historian 22 / M.Bearman - Tunnel vision
Jack Northrop’s all-metal Alpha design of 1930 was a classic example of a fuselage of what was then considered “good aerodynamic design” running into trouble over the wing. Note the small wing fillet, similar to that of the Hurricane.
-
Flight 1931-08 / Flight
The Northrop Alpha is an all-metal aircraft carrying 1,822 lb. useful load. Its cruising speed is 140 m.p.h. with a radius of 700 miles and 116 gall, of fuel. The engine is a Pratt and Whitney Wasp of 420 h.p. With a wing area of 295 sq. ft. the wing loading is 15 25 lb. h.p. and the power loading 10 7 lb./h.p. It is probably one of the most efficient American transport aircraft and has accommodation for 7 passengers.
-
Мировая Авиация 208
Самолеты Alpha были рассчитаны на трех пассажиров и 211 кг почты и груза.
-
Flight 1931-09 / Flight
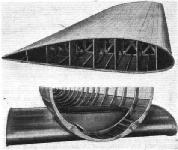
The flat plate multicellular type of wing construction and manner in which the Alclad skin is built up over ring-shaped bulkheads in the fuselage.
-
Flight 1931-09 / Flight
General arrangement drawings of the Northrop Alpha as a land and seaplane.
- Фотографии