Northrop. Самолеты схемы "Летающее крыло"
<...>
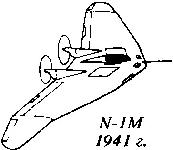
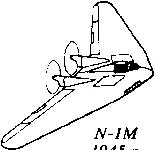
Опыт, приобретенный при разработке, пригодился через 10 лет, когда Джон Нортроп решил развить свои идеи "летающего крыла". В итоге в 1940 году в воздух поднялся самолет Northrop N-1M с двумя двигателями Lycoming мощностью по 65 л.с., установленными в толстом крыле и работавшими на толкающие воздушные винты. Схему N-1M уже можно отнести к "летающему крылу", а малое лобовое сопротивление самолета позволяло развивать ему высокую скорость как в пикировании, так и при планировании. При этом машине на взлете требовалось значительно меньше мощности, чем самолету такого же размера и массы, нетрадиционной схемы конструкции. Первые испытания выявили ряд проблем, главной из которых являлось охлаждение двигателя. Ее решили установкой моторов Franklin мощностью 120 л. с., работавших на трехлопастные воздушные винты. N-1M дожил до наших дней и находится в Национальном аэрокосмическом музее США.
<...>
- Описание
Фотографии
-
Air Enthusiast 1996-07 / A.Pelletier - Towards the ideal aircraft? (1)
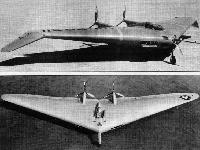
The Northrop N-1M in its initial configuration. This proof-of-concept prototype featured adjustable dihedral of outer-wing panels from 6° to 12°, adjustable sweep back from 26°46’ to 41°46’, and adjustable wingtip dihedral from 0° to -30°.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1974-01 / B.Gunston - The all-wing Northrops (1)
View of the N-1M. Picture shows it in "ruptured weather-racked duck" configuration and powered by two 120 h.p. Franklyn engines.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-04 / Plane facts
Регистрационный номер: NX28311 [3] The Northrop N1M in its original configuration with drooped wing tips incorporation the ailerons.
-
OS 1 / H.Cowin - X-Planes
The Northrop N-1M flew initially on 3 July 1940 and was 'Jack' Northrop's first true flying wing design. Strictly company funded to extend Northrop's knowledge of the subject, the N-1M was a small, low powered machine constructed of wood so as to be readily modifiable. The N-1M, as seen here in its early form, was powered by two 65hp Lycoming 0-145s driving pusher propellers and carried anhedral, or downward-canted wingtips. Later fitted with 120hp Franklin radials, the machine had its wingtip straightened out and flew with no significant deterioration in stability. In its later guise, top level speed reached 200mph. AII of the early test flying, including the first flight, had been done by Vance Breeze, the famed freelance test pilot, followed by Moye Stephens, doubling as test pilot from his normal role as Company Secretary. At the end of 1941, the sole N-IM, NX-28311 retired with over 200 flights logged.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-11 / Talkback
Регистрационный номер: NX28311 [3] The Northrop N1M in its initial configuration, showing the control surfaces in the downturned wingtips, undergoing weight and balance checks at the main Hawthorne plant, early 1940.
-
Авиация и Время 2008-06 / А.Чечин, Н.Околелов - "Летающие крылья" Нортропа (1)
Регистрационный номер: NX28311 [3] Экспериментальный самолет N-1M с отогнутыми и выпрямленными законцовками крыла
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1947 / All the world's aeroplanes
The Northrop N-1M Experimental tail-less Monoplane which first flew in 1940.
-
Air International 1984-06
The N-1M in final form
-
Мировая Авиация 208
N-1M стал продолжением работ, начатых по Avion 1, и был уже полноценным самолетом, созданным по схеме "летающее крыло". Вначале он оснащался двумя моторами Lycoming O-145 мощностью по 65 л. с., а затем - двигателями Franklin мощностью по 120 л. с. (на фотографии).
The Northrop N1M in its later form, with no anhedral on the wing tips. -
Aeroplane Monthly 1974-01 / B.Gunston - The all-wing Northrops (1)
View of the N-1M. Picture shows aircraft with planform approaching that of the later B-35 and YB-49. More than 200 flights were made with this aircraft.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1974-01 / B.Gunston - The all-wing Northrops (1)
View of the N-1M. Picture shows aircraft with planform approaching that of the later B-35 and YB-49. More than 200 flights were made with this aircraft.
-
Air Enthusiast 2003-07 / F.Allen - Before the B-2
Jack Northrop (right) and test pilot, Moye Stephens, with their N-1M.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-11 / Talkback
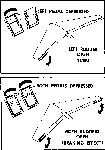
Two illustrations from the original Northrop brochure describing the operation of split surfaces.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-04 / Plane facts
The Northrop N1M in its original configuration with drooped wing tips incorporation the ailerons.
- Фотографии