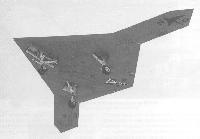
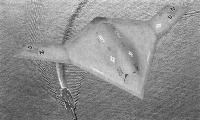
Northrop Grumman X-47
Серия БЛА X-47 была построена в рамках программы UCAS-D (Unmanned Combat Air System Demonstration), ставившей целью создание беспилотного палубного реактивного самолета для ВМС США. Позднее она превратилась в объединенную программу ВВС и ВМС JCAS (Joint Unmanned Combat Air Systems). Самолет X-47A Pegasus был демонстратором технологий, его постройка была профинансирована компанией-разработчиком. Опытная машина совершила первый полет 23 февраля 2003 года. X-47A выполнен по схеме "бесхвостка" с надфюзеляжным воздухозаборником, питающим ТРДД Pratt & Whitney Canada JT15D-5C. Хотя и выполненный с широким использованием технологий малозаметности (стелс), самолет имеет обычное выхлопное сопло, что, очевидно, сделано для снижения стоимости. Машина унаследовала многие особенности самолетов "Northrop Grumman", в особенности B-2 Spirit.
Два демонстратора X-47B, совершившие первый полет в 2011 году, отличаются от X-47A большими размерами и новой конструкцией внешней части крыла. X-47B будет использоваться для палубных испытаний и отработки автономной дозаправки в полете. Предлагается еще больший по размерам вариант X-47C, способный нести до 4535 кг боевой нагрузки.
- Описание
Фотографии
-
Air International 2002-06 / Airscene
Northrop Grumman’s X-47A Pegasus UAV prototype has been undergoing intensive testing and integrating of avionics and software at El Segundo, California, where it is seen here on March 26, 2002, as the aircraft prepares for its first flight. The aircraft conducted its third engine run on March 16, after previous runs in December and January, while on April 18 a successful autonomous start and shutdown of the P&W JT15D engine was achieved and repeated several times. The UAV is scheduled to move to the Naval Weapons Center, China Lake, California, for its first flight later this year.
-
Air International 2012-01 / News
Два прототипа X-47B на авиабазе «Патаксент-Ривер»
The two X-47Bs side by side at Edwards AFB, California, with AV-2 on the right.
Inset: The second X-47B UCAV making its maiden flight on November 22, 2011 at Edwards AFB, California. Of note on the nose landing gear door is the Pratt & Whitney badge (responsible for the powerplant) and skunk emblem of Lockheed Martin's Advanced Development Programs ('Skunk Works', involved in the design of the low observable aerodynamic edges, inlet lip and control surfaces, and development of the arrestor hook). -
Air International 2012-09 / News
The second Northrop Grumman X-47B Unmanned Combat Air System Demonstrator (AV-2, BuNo 168064/'502') has completed its first flight from NAS Patuxent River, Maryland, following its transfer from Edwards AFB, California. The 35-minute flight was made on July 29, 2012, during which it flew up to 7,500ft (2,286m) and 180kts (333km/h) over the nearby Chesapeake Bay. AV-2 arrived at the naval air station in June, joining AV-1, which has been there since December 2011.
-
Air International 2011-03 / News
БЛА по схеме "летающее крыло". В 1999 году "Boeing" получила контракт на постройку двух БЛА-демонстраторов технологий X-45A. Не пошедший в серию БЛА был создан по схеме "бесхвостка", его планер был выполнен из алюминиевых сплавов, а все внешние части и покрытие - из композитов (серийные машины планировалось строить почти полностью из композитов). Также не пошедший в серию Lockheed Martin RQ-3 Darkstar представлял собой достаточно большой БЛА. Он поднялся в воздух в 1996 году, но результаты испытаний оказались удручающими. В 2003 году в воздух поднялся БЛА X-47, сегодня он проходит испытания в рамках отработки концепции боевого БЛА. В интересах ВМС США аналогичные испытания проходит БЛА X-47B (на фото), совершивший первый полет в начале 2011 года. БЛА RQ-170 разработан "Lockheed Martin", применялся в Афганистане (где был впервые сфотографирован), а в конце 2011 года во время одного из заданий упал на территории Ирана. Информация по аппарату практически отсутствует. 27 апреля 2011 года первый полет выполнил еще один БЛА, созданный "Boeing", - X-47C Phantom Ray.
Airborne - the X-47B takes off and flies for the first time at Edwards AFB, California on February 4, 2011. The aircraft flew for 29 minutes during the flight test. -
Air International 2012-04 / News
Funding continues for the development of the X-47 unmanned combat aerial demonstration (UCAS-D) project to develop technology to operate a fixed-wing UAS from an aircraft carrier in 2013.
-
Air International 2013-01 / The Aviation World in 2013
В 2013 году начнется наиболее интересный этап программы - автономные палубные испытания. Как видно на этом снимке, носовая стойка X-47 оснащена всеми элементами, необходимыми для старта с катапульты.
-
Air International 2012-01 / News
The second X-47B Unmanned Combat Air System Demonstrator built by Northrop Grumman will be used to show the technology required to air-refuel an unmanned aerial vehicle from a manned tanker aircraft in 2014.
-
Air International 2011-11 / News
The X-47B UCAS-D during the test flight conducted on September 30, 2011.
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2015-11 / А.Бежко - Беспилотники
X-47B - современный американский БЛА, выполненный по технологии «стелс»
-
Мировая Авиация 210
Сходство с бомбардировщиком B-2A Spirit хорошо заметно на снимке одного из X-45B, летящего над Калифорнией. Пока остается неясным, пойдет ли этот БЛА в серию.
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2023-08 / В.Бакурский - Новые реалии войны в воздухе
БПЛА X-47B подходит к заправочному шлангу воздушного танкера
-
Air International 2015-06 / News
Unmanned Combat Aerial System Demonstrator X-47B BuNo 168064/'502’ completed the first air-refuelling with a manned tanker on April 22, 2015.
-
Air International 2015-11 / Pax: Home of US Navy flight testing
X-47B AV-2 receives fuel from Omega's Boeing 707 tanker N707MQ (c/n 21368) while operating in the Atlantic Test Ranges over the Chesapeake Bay. The test on April 22, 2015 marked the first time an unmanned aircraft refuelled in flight.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Boeing Boeing 707/720 - США - 1954
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2020-07 / Ю.Кузьмин - Дозаправка в воздухе: от первых опытов к первому в мире беспилотному заправщику
Дозаправка палубного ударного БЛА X-47B в воздухе
-
Air International 2015-11 / Pax: Home of US Navy flight testing
X-47B выполняет прием топлива от самолета-заправщика
X-47B AV-2 and Omega's Boeing 707 tanker, N707MQ (c/n 21368) over the Chesapeake Bay near to Naval Air Station Patuxent River.Другие самолёты на фотографии: Boeing Boeing 707/720 - США - 1954
-
Авиация и Время 2016-03 / А.Совенко - XXI век. В небе - роботы (1)
Первая дозаправка в полете X-47B в ходе испытательной программы Atlantic Test Ranges. 22 апреля 2015 г.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Boeing Boeing 707/720 - США - 1954
-
Air International 2015-06 / News
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Boeing Boeing 707/720 - США - 1954
-
Мировая Авиация 202
16 декабря 2008г.: в Палмдейле, Калифорния, состоялась выкатка первого из двух прототипов БЛА "Northrop Grumman" X-47B UCAV. Прототипы построены в рамках программы ВМС США Unmanned Combat Air System - Demonstration (UCAS-D) no созданию БЛА палубного базирования и отработки технологии автономной дозаправки БЛА в воздухе.
-
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
Steam builds up as X-47B BuNo.168063/'501‘ (AV-1) waits to be shot from the TC-7 catapult at Pax River, Maryland, on November 29, 2012. This was the first cat shot performed by an X-47B.
-
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
Sailors attach AV-2 to catapult two on the USS George Bush.
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2020-07 / Ю.Кузьмин - Дозаправка в воздухе: от первых опытов к первому в мире беспилотному заправщику
X-47B, отслеживая команды палубного руководителя, выруливает на старт
-
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
Sailors aboard the USS George Bush remove the chocks from X-47B AV-2 ready for the type's first cat shot on May 14, 2013.
-
Air International 2015-11 / Pax: Home of US Navy flight testing
Northrop Grumman's X-47B UCAS-D launches from the USS Theodore Roosevelt (CVN 71) in August 2014 during tests demonstrating its ability to operate safely and seamlessly with manned aircraft.
A shooter signals lor X-47B AV-1 to launch from the flight deck. -
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
Touch and go on the flight deck of the USS George Bush on May 17, 2013.
-
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
AV-2 shoots off the edge of the flight deck during the first cat shot made by an unmanned air vehicle from a US Navy super carrier on May 14, 2013.
-
Авиация и Время 2015-02 / А.Хаустов - Бумеранг эпохи "хай-тек"
Первый взлет X-47B с авианосца «Джордж Буш». 14 мая 2013 г.
-
Air International 2015-11 / Pax: Home of US Navy flight testing
Unmanned X-47B AV-1 launches from the aircraft carrier USS Theodore Roosevelt.
-
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
AV-2 passes over the flight deck following it's first practise approach to the USS George Bush.
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2020-07 / Ю.Кузьмин - Дозаправка в воздухе: от первых опытов к первому в мире беспилотному заправщику
БЛА X-47B над палубой авианосца
Touch and go on the flight deck of the USS George Bush on May 17, 2013. -
Air International 2017-10 / Airscene
The X-47B moments from touch down on the USS Theodore Roosevelt during a test period in August 2014.
To date, the X-47B Unmanned Combat Air System is the only unmanned air vehicle to have operated from a US Navy super carrier. -
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
AV-2 rolls down the flight deck during a touch and go aboard the USS George Bush.
-
Air International 2017-11 / Airscene
An X-47B Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle demonstrator, like this one seen landing aboard the aircraft carrier USS Theodore Roosevelt (CVN 71) during trials in August 2014, has been modified as a testbed for the future MQ-25 Stingray Carrier Based Air Refueling System
-
Air International 2013-08 / News
Northrop Grumman X-47B BuNo 168064/'NG-502' (AV-2) makes history as it catches number three wire on the deck of USS George H W Bush on July 10, 2013.
-
Air International 2015-11 / Pax: Home of US Navy flight testing
X-47B BuNo 168063/501 (c/n AV-1) takes the number one wire aboard the USS Theodore Roosevelt.
-
Air International 2015-11 / Pax: Home of US Navy flight testing
X-47B BuNo 168064/502 (c/n AV-2) was fitted with an air refuelling probe and an infrared camera system capable of providing precise navigation updates to get the air vehicle into the tanker's moving basket.
-
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
AV-2 being tow in the hangar bay aboard the Bush.
-
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
Sailors move X-47B AV-2 onto an aircraft elevator aboard the USS George Bush on May 14, 2013. Within hours of this image being taken, AV-2 successfully completed the type's first cat shot from a carrier flight deck.
-
Air International 2015-11 / Pax: Home of US Navy flight testing
Prior to embarking on board the USS Theodore Roosevelt, AV-1 had an automatic wing-fold capability introduced into its software enabling the wings to be automatically folded after landing.
-
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
Sailors assigned to the USS Harry S Truman and personnel from the UCAS integrated test team perform maintenance on AV-2.
-
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
X-47B AV-2 on the flight deck of the USS Harry S Truman on December 11, 2012.
-
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
X-47B AV-2 taxies on the flight deck of USS Harry S Truman during the type's first embarkation on December 9, 2012.
-
Air International 2015-11 / Pax: Home of US Navy flight testing
X-47B BuNo 168063/501 on the number one catapult prior to launch from the USS Theodore Roosevelt.
-
Air International 2015-11 / Pax: Home of US Navy flight testing
AV-1 on the Roosevelt's number one catapult alongside an F/A-18F Super Hornet during manned and unmanned flight operations.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: McDonnell Douglas F/A-18F Super Hornet - США - 1995
-
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
X-47B AV-2 was lifted aboard the flight deck of the USS George Bush at Naval Base Norfolk, Virginia on May 6, 2013. The air vehicle undertook the type's first carrier-borne cat shot eight days later.
-
Air International 2013-07 / M.Ayton - Embarked Unmanned & Unbelievable /Military/
The control display unit or CDU is classed as a mission control station and had to be certified just like an aircraft's cockpit requires certification to fly. The CDU can be likened to a mission control station on the deck operator's arm that requires a high redundancy system to ensure the safety and control required for moving an air vehicle on a flight deck. It was certified, through the standard airworthiness certification process, to be one of the types of controller used to control the air vehicle either at a land base or during embarkation on a carrier. The CDU features controls for the throttle and the brakes, for moving the air vehicle quickly and precisely into the catapult for launch, or out of the landing area following recovery, rolling the air vehicle forward and conducting tight turns. It also has push-button controls for the engine, BIT checks, folding and unfolding the wings, and lowering and retracting the hook; any function required on the flight deck. The CDU also includes a belt pack that holds the batteries and redundant digital modems that connect in with the air vehicle.
-
Авиация и Время 2015-02 / А.Хаустов - Бумеранг эпохи "хай-тек"
Опытный «беспилотник» X-47A
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2005-12 / Новости мировой авиации
Беспилотный X-47
-
Авиация и Время 2006-04 / А.Совенко - Жаркие дни "Фарнборо-2006"
Один из первых в мире ударных палубных БПЛА X-47
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2009-02 / Новости мировой авиации
Выкатка первого X-47B
-
Авиация и Время 2015-02 / А.Хаустов - Бумеранг эпохи "хай-тек"
Подготовка к взлету X-47B с наземной катапульты на авиабазе "Патаксент-Ривер"
-
Авиация и Время 2011-01
Палубный беспилотный самолет X-47B, разработанный компанией Northrop Grumman.
-
Авиация и Время 2015-02 / А.Хаустов - Бумеранг эпохи "хай-тек"
X-47B в проходе над авианосцем «Джордж Буш». 17 мая 2013 г.
-
Авиация и Время 2015-02 / А.Хаустов - Бумеранг эпохи "хай-тек"
Первая посадка X-47B на авианосец. 10 июля 2013 г.
-
Авиация и Время 2013-03
14 мая 2013г. палубный "беспилотник" X-47B UCAS-D выполнил первый катапультный взлет с авианосца George H.W. Bush (CVN 77), находившегося у побережья Вирджинии. БПЛА стартовал в 11.18, выполнил несколько запланированных подходов к авианосцу на малой высоте, после чего приземлился на авиабазе ВМС Патаксент Ривер. Полет длился 65 мин."Сегодня мы увидели небольшой, но существенный элемент будущего нашего военного флота: мы начинаем интеграцию беспилотных систем, возможно, в самую сложную боевую среду, которая существует сегодня - на полетную палубу атомного авианосца", - проком ментировал это событие вице-адмирал Дэвид Басс (David Buss), командующий авиацией ВМС США. По контракту с военно-морскими силами компания Northrop Grumman спроектировала, построила и испытала два экземпляра X-47B. Первый взлет с палубы выполнил второй из них. Посадка X-47B на авианосец с использованием аэрофинишера запланирована на конец лета.
-
Авиация и Время 2015-02 / А.Хаустов - Бумеранг эпохи "хай-тек"
X-47B на ангарной палубе авианосца «Джордж Буш»
-
Авиация и Время 2015-02 / А.Хаустов - Бумеранг эпохи "хай-тек"
Частотные испытания X-47B
-
Авиация и Время 2015-02 / А.Хаустов - Бумеранг эпохи "хай-тек"
Пост управления беспилотными аппаратами X-47B на авианосце «Гарри Трумэн»
-
Air International 2011-01 / L.Nordeen, D.Isby - Rise of the UAV /Military/
Artist's impression of an X-47B unmanned combat air vehicle (UCAV) making an arrested landing on a US Navy carrier. One of the potential advantages of carrier UCAV operations is that landings could be made automatically or each UAV could be 'flown' to the deck by a single pilot in turn, reducing the need for carrier pilot training.
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2008-07 / Новости мировой авиации
Рисунок палубного ударного БЛА NUCAS
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2009-02 / Новости мировой авиации
Проектный вид X-47B на палубе авианосца
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2010-08 / Новости мировой авиации
Рисунок БПЛА, создаваемого на основе демонстратора технологий Нортроп Грумман X-47B
- Фотографии