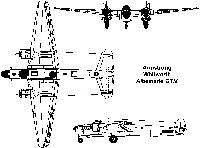
Albemarle / A.W.41
"Албемарл" создан в КБ фирмы "Армстронг-Уитворт эйркрафт" под руководством Дж. Ллойда первоначально как средний бомбардировщик AW.41. Это был двухмоторный моноплан смешанной конструкции с двухкилевым оперением, убирающимся трехколесным шасси с носовой стойкой. Его опытный образец под названием "тип 208" совершил первый полет 20 марта 1940 г. Производство этих машин на заводе "Армстронг-Уитворт" в Хоксли начали в сентябре 1941 г., перейдя на серийный выпуск в декабре. Бомбардировщики "Албемарл" B.I поступили на вооружение британских ВВС фактически только в августе 1942 г. и не получили широкого распространения. В октябре 1942 г. произвели пробную переделку B.I в военно-транспортный самолет ST.I ("тип 217"). Следом за этим подобную модификацию стали осуществлять серийно на заводе в Хоксли и мастерских в Лайнехэме и Кембридже. С апреля 1945 г. завод начал строить в массовых количествах буксировщики планеров GT.II. Всего выпустили 572 транспортных "албемарла", в т.ч. 42 переделанных бомбардировщика.
Экипаж - 4 чел. (транспорт), 5 чел. (бомбардировщик). Моторы "Геркулес" XI. Вооружение 6x7,69, бомбы до 1500 кг (бомбардировщик), 4x7,69 (варианты GT), 2x7,69 (варианты ST), 1x7,62 (переделка части самолетов ST.I (SF) в СССР). Грузоподъемность вариантов ST и GT - 2100 - 2400 кг.
Транспортные "албемарлы" состояли на вооружении в Великобритании с ноября 1942 г., в Советском Союзе - с марта 1943 г.
Серийно выпускались следующие модификации:
- "Албемарл" B.I, бомбардировщик;
- "Албемарл" ST.I, переделка B.I в грузовой самолет (введена грузовая дверь справа), выпускались также мало отличавшиеся от них ST.I (SF) (он же "тип 219") - экспортный для СССР без вооружения и GT.I с устройством для буксировки десантных планеров;
- "Албемарл" GT.II, транспортный самолет-буксировщик планеров специальной постройки, выпускались также GT.IIa, отличавшиеся по оборудованию, и ST.II (без буксировочного устройства);
- "Албемарл" GT.V и ST.V- усовершенствованные варианты с улучшенным оборудованием и аварийным сливом горючего в полете;
- "Албемарл" GT.VI и ST.VI с грузовой дверью слева, GT.VI серии 2 имел вооружение 2x7,69, как и у всех ST.VI.
Бомбардировщики B.I сделали всего один боевой вылет с бомбами - в феврале 1943 г. на цели во Франции. С ноября 1942 г. B.I как транспортные машины начали летать на трассе до Гибралтара. С января 1943 г. в британские ВВС стали в массовых количествах поступать GT.I и ST.I. С марта их применяли в Северной Африке. В июне вместе с самолетами модификации II с их помощью высадили на Сицилии комбинированный парашютно-планерный десант. В июле подобную операцию провели в Южной Франции. Далее "албемарлы" участвовали во всех крупных высадках воздушных десантов - в Нормандии в июне 1944 г., под Арнемом в сентябре, при пересечении Рейна. Линию на Гибралтар "албемарлы" обслуживали до марта 1944 г. В конце войны они служили и в учебных частях.
Советский Союз получил партию транспортных "албемарлов" весной 1943 г. Они использовались 1-й транспортной дивизией ГВФ для перевозок срочных грузов в тылу, а ВВС и морской авиацией - как учебные самолеты.
"Албемарл" был снят с производства в декабре 1944 г. В Англии они служили до августа 1947 г., в Советском Союзе последние машины списали в конце 1945 г.
"Албемарл" ST.I||
Размах:||23,46 м
Длина:||18,28 м
Моторы, количество х мощность:||2x1590 л.с.
Взлетная масса, максимальная:||16556 кг
Максимальная скорость:||427 км/ч
Практический потолок:||5485 м
Дальность:||2090 км
Описание:
- Albemarle / A.W.41
- Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation
Фотографии
-
Aviation Historian 14 / R.Flude - The Molotov Express
Originally conceived as a medium reconnaissance-bomber made from non-strategic materials, the Albemarle started life as a Bristol design, the type’s heritage in terms of its general configuration and distinctive Blenheim-type scalloped nose being much evident; but the aircraft proved inferior to the RAF types it was meant to replace, and it was quickly relegated to general duties in service.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-08 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (1)
Регистрационный номер: P1361 [7] The Albemarle I second prototype, P1361, photographed on August 3, 1942, while serving with No 5 Pilot's Advanced Flying Unit at Tern Hill.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1996-08 / D.Webb - Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle /Tested & failed/
Регистрационный номер: P1361 [7] Further view of the second prototype Albemarle. The design originated as the Bristol 155 and the Albemarle’s nose bore a marked resemblance to that of the Bristol Blenheim IV.
-
Aviation Historian 35 / M.Bearman - The other sound barrier
Built to Air Ministry Specification B.18/38 for a “Reconnaissance Bomber for Rapid Production”, the Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle was powered by a pair of Bristol Hercules radials of considerably less power than the Manchester’s Vultures - yet it was even noisier for its crew. Was the problem similarly propeller-based?
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1996-08 / D.Webb - Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle /Tested & failed/
Регистрационный номер: P1361 [7] The two Albemarle prototypes, P1360 and P1361, the latter seen here, were constructed at Hamble in the Air Service Training Shops. Production aircraft were assembled at Brockworth by A. W. Hawksley Ltd.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1996-08 / D.Webb - Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle /Tested & failed/
Регистрационный номер: P1361 [7] The two Albemarle prototypes, P1360 and P1361, the latter seen here, were constructed at Hamble in the Air Service Training Shops. Production aircraft were assembled at Brockworth by A. W. Hawksley Ltd.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1996-08 / D.Webb - Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle /Tested & failed/
Further view of the second prototype Albemarle. The design originated as the Bristol 155 and the Albemarle’s nose bore a marked resemblance to that of the Bristol Blenheim IV.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-08 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (1)
Регистрационный номер: P1360 [2] The first Albemarle prototype, P1360, in April 1940, with short span wings and mass-balanced rudders
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1996-08 / D.Webb - Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle /Tested & failed/
Регистрационный номер: P1361 [7] P1361, the second prototype Albemarle, taken in April 1941. Note the small "bumper" tailwheel fitted to what was to be the first operational British aircraft to have a tricycle undercarriage.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-08 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (1)
Регистрационный номер: P1360 [2] The first Albemarle prototype, P1360, later the same year, with increased span and horn-balanced rudders.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1996-08 / D.Webb - Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle /Tested & failed/
Регистрационный номер: P1361 [7] The second prototype Albemarle, P1361, first flew on April 20, 1941. Note the small “bumper” tail wheel. Deliveries of production aircraft, assembled at Brockworth, began in September 1941.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1996-08 / D.Webb - Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle /Tested & failed/
Регистрационный номер: P1361 [7] P1361, the second prototype Albemarle, taken in April 1941. Note the small "bumper" tailwheel fitted to what was to be the first operational British aircraft to have a tricycle undercarriage.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-08 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (1)
Регистрационный номер: P1363 Early production Albemarle B.I P1363. Deliveries from Brockworth began in September 1941. This aircraft later served with 42 OTU, becoming instructional airframe 4450M in January 1944.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-08 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (1)
Регистрационный номер: V1599 V1599, the last of 90 Albemarle GT Is, served as the prototype ST I special transport variant, and was tested with a long-travel undercarriage in 1943.
-
Моделист-Конструктор Военно-транспортные самолеты Второй мировой войны
"Албемарл" I британских ВВС
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1985-05 / T.Neil - Another job for Burgoyne (3)
“It crouched there on its tricycle undercarriage, a menacing, darkly camouflaged shape. ”
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1985-05 / T.Neil - Another job for Burgoyne (3)
Регистрационный номер: P1653 [2] The 77ft span Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle was powered by two 1,590 h.p. Bristol Hercules XI engines and weighed 22,600 lb fully loaded. It normally flew with a crew of four.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-09 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (2)
Регистрационный номер: P1653 [2] Factory-fresh Albemarle ST I P1653 is overflown by another of its kind. Note the tail guards to prevent parachute lines fouling the elevators.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1980 / Encyclopedia of Aviation - Aircraft A-Z - v2
Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle II troop carrier.
-
Air-Britain Aeromilitaria 1983-02 / Dunlop's Test Flight
Albemarle IV at Honiley in 1945 running-up. The turret and guns are still fitted in the dorsal position
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1946 / 03 - All the world's aeroplanes
The Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle I (two Bristol Hercules XI engines).
-
Aviation Historian 14 / R.Flude - The Molotov Express
One of the 14 Albemarles despatched to the Soviet Union by No 305 FTU at RAF Errol. Two of these, P1455 and P1645, were lost en route and another, P1647, had to return following oilfeed problems. It was, however, fixed and sent again.
-
Моделист-Конструктор Военно-транспортные самолеты Второй мировой войны
"Албемарл" на испытаниях в НИИ ВВС, 1943 г.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-09 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (2)
One of 12 Albemarle ST Is allotted to the USSR in 1944. Note freight door and sliding dorsal hood.
-
Моделист-Конструктор Военно-транспортные самолеты Второй мировой войны
"Албемарл" перед перегонкой в СССР, авиабаза Эррол (Шотландия), 1943 г.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-09 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (2)
Регистрационный номер: V1624 An Albemarle ST II, probably V1624 later of 297 and 570 Squadrons, makes a low and slow flypast for the press, January 1944.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-09 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (2)
Sleek lines belied poor performance.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-09 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (2)
Регистрационный номер: V1823 STV V1823 in 297 Squadron markings as P5-S, with crudely-applied invasion stripes.lt crashed near Bretton, Wilts, while towing a glider on December 22, 1944, serving with 22 HGCU.
-
Моделист-Конструктор Военно-транспортные самолеты Второй мировой войны
"Албемарл" V из 297-й эскадрильи британских ВВС, июнь 1944 г. В хвостовой части фюзеляжа - устройство для буксировки планеров
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1946 / 03 - All the world's aeroplanes
The Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle II Glider-tug and Paratroop Transport (two Bristol Hercules XI engines).
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1979-11 / D.Middleton - Airspeed's Silent Warhorse (2)
A Horsa under tow, as seen from the gunner’s position of an Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Airspeed Horsa / AS.51 - Великобритания - 1941
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1979-11 / D.Middleton - Airspeed's Silent Warhorse (2)
The shot shows the line falling away at the moment of release.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Airspeed Horsa / AS.51 - Великобритания - 1941
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1996-08 / D.Webb - Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle /Tested & failed/
Completed Armstrong Whitworth Albemarles awaiting delivery at Brockworth. The type was first used operationally by Nos 296 and 297 Sqns, during the invasion of Sicily on the night of July 9-10, 1943, when glider-borne troops were towed in Airspeed Horsas by Albemarles and Halifaxes taking part in Operation Husky.
-
Air-Britain Aeromilitaria 1983-02 / Dunlop's Test Flight
Line-up at Elmdon consists of a Lancaster I, Bristol Buckingham, Albemarle IV, Wellington III, the company's own Proctor V executive transport and, at the end of the line, a Lincoln I
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Avro Lancaster / Type 683 - Великобритания - 1941Avro Lincoln / Type 694 - Великобритания - 1944Bristol Buckingham / Type 163 - Великобритания - 1943Percival Proctor / P.28 - Великобритания - 1939Vickers Wellington / Type 271 - Великобритания - 1936
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-09 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (2)
Nearing completion, this Albemarle reveals details of engine mounting, wing leading edge and nosewheel.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-09 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (2)
Albemarle production by A. W. Hawkesley Ltd. In the foreground is a wing centre section, with nose sections to the left and fuselage centre and rear sections to the right.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-09 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (2)
A close-up of the power-operated Boulton Paul dorsal turret.
-
Aviation Historian 36 / M.Russell - A question of calibre
Four 0-303in Brownings in an aft-facing Boulton Paul Type A electrically operated dorsal turret fitted to an Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle. The Albemarle’s dorsal turret was offset slightly to port to allow space for a passageway through to the rear fuselage, and the fairing forward of the turret retracted automatically when the turret was trained to fire forwards. The Albemarle saw only very limited service.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-08 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (1)
The cockpit of an Albemarle ST V, showing the access to the nose "greenhouse" on the starboard side.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1985-05 / T.Neil - Another job for Burgoyne (3)
“Blimey! The Albert Hall! Front stalls or circle? Take your pick."
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1997-02 / Skywriters
Регистрационный номер: V1762 The wreckage of Albemarle V1762 after its crash at Sherburn-in-Elmet on October 21, 1944.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-08 / R.Williams - Unwanted Albemarle (1)
The Albemarle mock-up, completed in September 1938, showing the original Merlin-engined version.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1990-03
50th anniversary of the first flight of the Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle - March 20, 1940
-
Air-Britain Aeromilitaria 1976-01
P1390 MA-L, 161Sq, green/earth/black red codes
V1823 P5-S, 297Sq, green/earth/black red codes black/white bands
Russian aircraft with turret deleted. Freight doors fitted on st'b'd side Some RAF aircraft mod. to similar configuration. Green/earth/sky -
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1946 / 03 - All the world's aeroplanes
The Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle.
-
Моделист-Конструктор Военно-транспортные самолеты Второй мировой войны
Armstrong Whitworth Albemarle GT.V
-
Air-Britain Aeromilitaria 1976-01
AW.41 Albemarle
- Фотографии