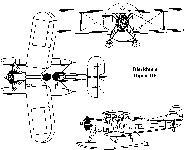
Описание
Страна : Великобритания
Год : 1926
Двухместный торпедоносец/бомбардировщик палубного и аэродромного базирования
Варианты
- Blackburn - Ripon / T.5 - 1926 - Великобритания
- Mitsubishi - B2M - 1928 - Япония
- Blackburn - Baffin / B-5 - 1933 - Великобритания
Ripon / T.5
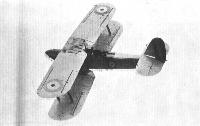
Торпедоносец, бомбардировщик и разведчик. Одномоторный биплан смешанной конструкции со сменным (поплавки/ колеса/лыжи) неубирающимся шасси. Создан в КБ "Блэкберн эйрплейн энд мотор компани" под руководством Ф. Бампаса первоначально как палубный разведчик-бомбардировщик и торпедоносец на базе конструкции более ранней машины "Велос". Опытный самолет Т.5 совершил первый полет 17 апреля 1926 г. На деревянные поплавки впервые установили второй опытный экземпляр, поднявшийся в воздух 12 августа. Серийное производство "райпонов" развернули на заводе "Блэкберн" в Бру в 1928 г. Серийные машины комплектовались как колесным, так и поплавковым шасси (с металлическими поплавками). Всего построено 92 экз.
В сентябре 1929 г. в Финляндию отправили образец экспортной модификации "Райпон" IIF. Ее в 1931 г. запустили в производство на заводе "Валтион лентоконетехдас" (VL) в Тампере. Там изготовили 25 самолетов со сменными шасси: колеса, лыжи или два поплавка. Машины финского производства отличались уменьшенной высотой вертикального оперения и фанерной обшивкой задней части фюзеляжа взамен полотняной обтяжки. Они не имели торпедной подвески.
"Райпон" состоял на вооружении британской морской авиации с августа 1929 г., финских ВВС - с сентября 1929 г.
Экипаж - 2 чел. Двигатель "Лайон" X, XI или XIA (самолеты английской постройки), GR 9Ak (1-я серия финской постройки), "Пантер" IIA (2-я серия финской постройки) или "Пегасус" IIM3 (3-я серия финской постройки). Вооружение 3x7,69 (с 1935 г. в Финляндии самолеты перевооружены пулеметами местного производства), бомбы до 400 кг.
Основные серийные модификации:
- "Райпон" IIA, палубный торпедоносец с мотором "Лайон" XI, только на колесах, вооружение 2x7,69, бомбы до 660 кг или одна торпеда весом 700 кг;
- "Райпон" IIF, экспортный вариант для Финляндии с мотором "Пантер" IIA, без палубного оборудования, сменное шасси (лыжи и поплавки изготовлялись заводом VL в Финляндии); вооружение 3x7,62, бомбы до 400 кг; поздние серии финской постройки имели двигатель "Пегасус" IIL3 (поплавковые) или "Пегасус" IIM3 (колесные);
- "Райпон" III, цельнометаллический палубный торпедоносец с мотором "Лайон" XIA, вооружение как у IIA.
Производство в Великобритании закончено в декабре 1933 г., в Финляндии - в 1936 г.
Британская морская авиация начала снимать "Райпон" с вооружения в январе 1934 г., к началу Второй мировой войны их не осталось даже в учебных подразделениях. Часть выпущенных машин поздних серий переделали в торпедоносцы "Баффин". В Финляндии к 1939 г. большая часть оставшихся в строю самолетов была модернизирована и оснащена моторами "Пегасус". В период советско-финской войны "райпоны" применялись как легкие бомбардировщики (дневные и ночные) и разведчики, в основном на колесах. С июня 1941 г. они использовались еще и как самолеты связи, санитарные; поплавковые машины использовались двумя эскадрильями для патрулирования прибрежных районов, разбрасывания листовок, перевозки раненых и различных грузов.
Финские ВВС окончательно сняли "Райпон" с вооружения в декабре 1944 г.
"Райпон" IIA ("Райпон" IIF)||
Размах:||13,67 м (13,67 м)
Длина:||11,21 м (10,99 м)
Моторы, количество х мощность:||1x570 л.с. (1x580 л. с.)
Взлетная масса, максимальная:||3362 кг (3391 кг)
Максимальная скорость:||203 км/ч (190 км/ч)
Практический потолок:||3965 м (2650 м)
Дальность:||(2070 км)
Описание:
- Ripon / T.5
- Blackburn Т.5 Ripon
- Flight, June 1929
BRITISH AIRCRAFT AT OLYMPIA
Фотографии
-
Flight 1927-10 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: N203 [2] THE BLACKBURN "RIPON": Fitted with Napier "Lion" engine, this machine is produced both as a seaplane and as a landplane
-
Flight 1928-01 / Flight
THE LATEST TYPE OF TORPEDO-PLANE: Three views of the Blackburn "Ripon II," fitted with Napier "Lion" engine. The Blackburn Co. has specialised on the production of torpedo-planes for many years, and the present type marks a very distinct advance. The machine can also be fitted with floats and operate as a seaplane.
-
Мировая Авиация 57
Торпедоносец/бомбардировщик Ripon мог нести на внешней подвеске 457-мм торпеду, на фотографии - Ripon Mk IIC.
-
Flight 1930-10 / Flight
Delegates interested in the torpedo on the Blackburn-Napier "Ripon."
-
Flight 1928-05 / Flight
Some of the distinguished visitors in front of the Blackburn "Ripon."
-
Flight 1928-05 / Flight
SOME BLACKBURN AEROPLANES "ON PARADE": Left to right, a "Cirrus-Bluebird," a "Genet-Bluebird," a "Lynx-Lincock," a "Napier" Ripon, and a "Napier-Dart."
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Blackburn Bluebird / L.1 - Великобритания - 1924Blackburn Lincock / F.2 - Великобритания - 1928Blackburn Swift T.1 / Dart T.2 - Великобритания - 1920
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1977-09 / Personal album
A visit to Abu Suier by a batch of aircraft from a Fleet Air Arm carrier. In the foreground is Fairey IIIF Mk III S1356, powered by the trusty Napier Lion (note the windsock on the rudder). The other five aircraft are Blackburn Ripon IIC torpedo bomber/reconnaissance aircraft, also Lion-powered.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Fairey Fairey IIIF - Великобритания - 1926
-
Flight 1932-06 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: N231 [4] -
Flight 1928-05 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: N231 [4] THE BLACKBURN "RIPON" TORPEDOPLANE: Fitted with a Napier "Lion" engine, this machine carries a 1,400 lb. torpedo, the placing of which is shown in above photographs which illustrate the machine from various viewpoints, with wings folded and spread.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1977-09 / Personal album
Регистрационный номер: S1656 A closer look at one of the visiting Ripon IICs, S1656, powered by a 50 h.p. Lion XIA, was delivered to Sealand between late 1931 and early 1932. A total of 31 Mk IICs were produced, this final Ripon variant having all-metal wings rigged with more sweepback than the composite wood and metal wings of earlier marks. This aircraft was one of 26 later converted to Baffins by installing the Bristol Pegasus II.M3 radial of 580 h.p., and it then went to No 811 Squadron bearing the code 612.
-
Flight 1931-03 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: S1272 [5] AIRCRAFT TYPES TO BE SEEN IN THE "EAGLE": 1, The Blackburn "Ripon" with Napier "Lion" engine.
-
Flight 1930-10 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: S1272 [5] For a number of years the Blackburn company has made a specialised study of the requirements to be met in the design of torpedo-carrying aircraft. These photographs show the latest type to be produced, the "Ripon III," which is of all-metal construction and fitted with a Napier engine. Note that the ailerons are inter-connected with Handley Page leading-edge slots.
-
Flight 1928-05 / Flight
The Blackburn "Ripon" with Napier "Lion X" engine, after taking off
-
Flight 1929-04 / Flight
"THROWING IT ABOUT": Capt. Blake, Blackburn's chief test pilot, putting the "Ripon" torpedoplane through its paces. The engine is a Napier "Lion." Note the Handley Page control slots, which are connected to the ailerons. A float undercarriage can be fitted.
-
Flight 1929-07 / Flight
BLACKBURN "RIPON" (Napier "Lion").
-
Flight 1930-10 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: S1272 [5] -
Flight 1930-02 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: S1272 [5] THE LATEST BLACKBURN MACHINE: Three aerial views of the all-metal "Ripon" Mark III Torpedoplane.
-
Flight 1928-05 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: N231 [4] The Blackburn "Ripon" with Napier "Lion X" engine, descending to near sea level, and finally dropping the torpedo. The pilot during this demonstration was Captain A. M. Blake.
-
Flight 1937-05 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: N231 [4] BLACKBURN "RIPON": Torpedo Carrier, with Napier "Lion" Engine.
-
Мировая Авиация 200
Торпедой, пли! Blackburn Ripon сбрасывает 457-мм торпеду. Торпедная атака была в те годы очень непростой и опасной задачей, но успешное ее завершение зачастую имело стратегические последствия.
-
Flight 1933-09 / Flight
TORPEDO ATTACK: A Blackburn "Ripon" of No. 811 (Torpedo Bomber) Squadron of the Blue Force delivering an attack on H.M.S. Malaya. H.M.S. Warspite, the Red flagship, is ahead.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1980 / Encyclopedia of Aviation - Aircraft A-Z - v2
Blackburn Ripon IIA.
-
Air-Britain Aeromilitaria 1980-03
A newly-landed Ripon awaits striking-down
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1997-12 / G.Tuff - A life in service
Another day at Gosport, with a torpedo being taken to its aircraft. Vildebeest Mk I S1712 stands behind, and the tail of a Ripon may be seen on the left.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Vickers Vildebeest / Type 132 - Великобритания - 1928
-
История Авиации 34 / О.Киселев - Истребители И-16 в Зимней войне 1939-1940гг. /Страницы боевой карьеры/ (3)
Регистрационный номер: RI-141 Неуклюжие и тихоходные легкие бомбардировщики "Райпон", составлявшие основу матчасти LLv 16, при встрече с советскими истребителями шансов уйти целыми и невредимыми практически не имели, поэтому боевые вылеты совершали только в плохую погоду или ночью.
-
Моделист-Конструктор Ближние разведчики, корректировщики и штурмовики Второй мировой войны
Регистрационный номер: RI-121 "Райпон" IIF финских ВВС, эскадрилья Lelv6, 1942 г.
-
Моделист-Конструктор Гидросамолеты Второй мировой войны
Финский "Райпон" IIF из звена 4/LeLv6,1943 г.
-
Моделист-Конструктор Гидросамолеты Второй мировой войны
Регистрационный номер: RI-159 "Райпон" IIF с мотором HS 12Nbr, 1939 г.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1984-10 / Personal album
In 1930 the prototype Vickers Vildebeest, N230, was modified for exhibition at the Paris Air Show. The original Jupiter XF engine was replaced with a Jupiter XIF with Townend ring. Registered G-ABGE for the show, the aircraft was modified further and flown on a sales tour of Baltic ports. This photograph was taken during the tour at Santahamina, Helsinki. A Finnish Air Force Blackburn Ripon is seen at right.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Vickers Vildebeest / Type 132 - Великобритания - 1928
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1984-10 / Personal album
Регистрационный номер: RI-151 In 1928 the Finnish Government purchased a Blackburn Ripon IIF to serve as a pattern aircraft for licence-building others in Finland. A total of 25 Ripons was built in Finland and the type served in the Finnish Air Force from 1929-45. During the war the Ripons were used on U-boat patrols, leaflet dropping and for evacuating casualties. Ripon RI-140 survives and has been preserved for a museum.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1938 / 02 - The progress of the world in military aviation during the year 1937-38
Blackburn "Ripon" Floatplanes of the Finnish Air Force.
-
Flight 1927-10 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: N204 THE BLACKBURN "RIPON": Fitted with Napier "Lion" engine, this machine is produced both as a seaplane and as a landplane. Note the water rudders on the heels of the floats in the seaplane version.
-
Flight 1931-01 / Flight
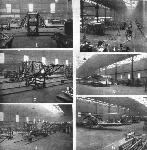
TRACK ASSEMBLY OF AIRCRAFT: These two photographs show the main sections of a Blackburn "Ripon." Above the central steel tube fuselage structure with petrol tank in place, and below the wooden rear portion of the fuselage. It is chiefly to the "Ripon" that the system of track assembly has been applied at Brough.
-
Flight 1931-01 / Flight
TRACK ASSEMBLY OF AIRCRAFT AT BROUGH: (1) First stage, a "Ripon" fuselage on the track. (2) The next stage, the rear portion of the fuselage added. (3) Beginning of track, and "Ripons" in early stages of assembly. (4) "Ripons" nearing end of track; note overhead derrick. (5) "Ripons" nearing completion on the end of the track. (6) The final stages. In the foreground a "Ripon" ready for test flights.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1986-11 / Personal album
Регистрационный номер: S1469 Lt Skene's Blackburn Ripon, S1469, biting the dust at Hal Far on August 7, 1931. The pilot was uninjured and the Ripon probably flew again.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1986-11 / Personal album
Регистрационный номер: K3548 A ditched 812 Squadron Blackburn Ripon off Malta on March 3, 1934. K3548 was converted to a Baffin and the type succeeded the Ripon as the FAA’s torpedo bomber, entering service in January 1934. The Ripon was powered by the in-line Napier; Baffins had the Pegasus radial
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1976-04
Регистрационный номер: S1652 Blackburn Ripon No 811 Squadron HMS Furious 1934
-
Flight 1929-07 / Flight
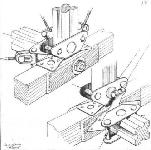
Fuselage fittings for wooden longerons on Blackburn "Ripon II."
-
Моделист-Конструктор Гидросамолеты Второй мировой войны
Blackburn Ripon IIF
- Фотографии