Варианты
- Northrop - YF-17 Cobra - 1974 - США
- McDonnell Douglas - F/A-18A Hornet - 1978 - США
- McDonnell Douglas - F/A-18B Hornet - 1979 - США
- McDonnell Douglas - F/A-18C Hornet - 1986 - США
- McDonnell Douglas - F/A-18D Hornet - 1987 - США
- McDonnell Douglas - F/A-18E Super Hornet - 1995 - США
- McDonnell Douglas - F/A-18F Super Hornet - 1995 - США
- Boeing - EA-18G Growler - 2006 - США
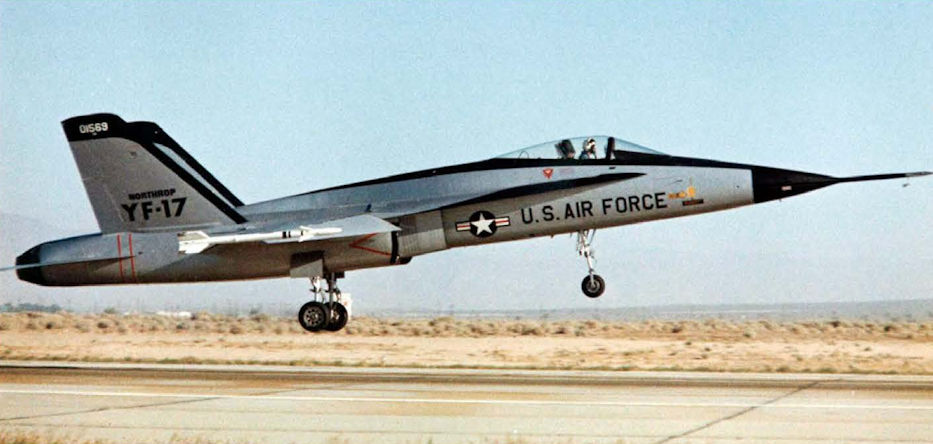
Northrop YF-17
В инициативном порядке компания разработала перспективный боевой самолет под обозначением Northrop P-530 Cobra. Когда ВВС США объявили конкурс на прототип легкого истребителя, "Northrop" предложила самолет P-600, в котором использовались многие новинки аэродинамики и силовая установка, предназначавшиеся для P-530. Из четырех полученных проектов ВВС США выбрали предложения компаний "General Dynamics" и "Northrop", поручив каждой из них построить по два прототипа под обозначениями YF-16A и YF-17A, соответственно. Два прототипа YF-17A поднялись в воздух 9 июня и 21 августа 1974 года. Особенностями компоновки YF-17A были отклоненные наружу поверхности вертикального оперения и развитые корневые наплывы крыла. Во время испытаний по программе LWF/ACF два YF-17 в ходе 288 полетов налетали 345,5 часов (в том числе 13 часов на сверхзвуке), а конкурирующей пары YF-16 в ходе 330 полетов - 417 часов. Во время испытательных полетов YF-17 выходил на углы атаки до 63° и продемонстрировал скольжение с углом до 36° при угле атаки 40°. Однажды один из самолетов совершил семь полетов за семь часов - при этом среднее время подготовки к вылету составило 15 минут. Несмотря на эти впечатляющие результаты, ВВС выбрали General Dynamics F-16. Испытания прототипа YF-17A, проведенные ВМС США, привели к доработкам самолета в соответствии с требованиями моряков. Так как "Northrop" не имела опыта создания палубных истребителей, было принято решение подключить к программе фирму "McDonnell". В тот период планировалось, что "McDonnell Douglas" будет отвечать за продажи палубного варианта машины, a "Northrop" - сухопутного. Но McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet, созданный в результате совместных работ, ныне базируется не только на палубах авианосцев, но и на береговых аэродромах.
ТАКТИКО-ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЕ ХАРАКТЕРИСТИКИ
Northrop YF-17A
Тип: одноместный экспериментальный истребитель
Силовая установка: два ТРДФ General Electric YJ101-GE-100 тягой по 64,08 кН на форсаже
Летные характеристики: максимальная скорость на высоте 12192 м - 2124 км/ч; потолок 18 288 м; максимальная дальность полета 4500 км
Масса: пустого 9527 кг; максимальная взлетная 13894 кг
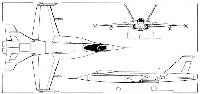
Размеры: размах крыла 10,67 м; длина 16,92 м; высота 4,42 м; площадь крыла 32,51 м2
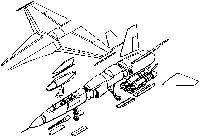
Вооружение: одна 20-мм пушка M61 Vulcan и две ракеты AIM-9 Sidewinder на пусковых устройствах на законцовках крыла; возможность установки двух пилонов под крылом для бомб Mk 84
- Описание
Фотографии
-
Мировая Авиация 129
Northrop YF-17. Предшественником F/A-18 был YF-17, принимавший участие в конкурсе на легкий истребитель для ВВС США; конкурс выиграл General Dynamics F-16. Изображен второй из двух YF-17, окрашенный в "камуфляж ПВО" из двух оттенков серого цвета.
-
Мировая Авиация 175
YF-17 №2, LWF/ACF Joint Test Force. Построено два YF-17. Изображен второй самолет - 72-1570, первый - 72-1569. Сегодня эта машина находится в Мемориальном парке линкора "Алабама".
-
Мировая Авиация 210
Вторая опытная машина Northrop YF-17 во время совместных испытаний по программе LWF/ACF, проходивших на авиабазе Эдвардс в Калифорнии в 1974 году. Обратите внимание на камуфляжную окраску, нанесенную только на второй самолет.
-
Мировая Авиация 9
На опытном истребителе YF-17 был использован наплыв с очень большой хордой. Сложная аэродинамика крыла была дополнена еще и аэродинамической круткой передней кромки.
Проиграв конкурс ВВС, компания "Northrop" предложила самолет YF-17 ВМС США. На снимке - первый самолет во время летных испытаний уже с надписью NAVY на борту. -
Мировая Авиация 113
Хотя YF-17 был отличным истребителем, он проиграл конкурс ACF, проводимый ВВС США. Однако фирма "McDonnell Douglas" полностью реализовала потенциал самолета, превратив его в F/A-18 для ВМФ.
-
Мировая Авиация 117
Новый легкий истребитель ВВС США. В конкурсе на легкий истребитель для ВВС США, кроме YF-16A, принимал участие Northrop YF-17 (фото), выполнивший первый полет 9 июня 1974г. Хотя YF-17 и проиграл, на его основе "Northrop" и "McDonnell Douglas" разработали двухдвигательный F/A-18 Hornet, который 2 мая 1975 года вышел победителем в конкурсе на самолет для ВМС и КМП США.
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2024-08 / М.Никольский - Рождение F-16 (5)
YF-16 (на снимке с конкурентом YF-17) проводит испытания новых систем управления, в том числе боковой РУ. Он стал первым истребителем с ЭДСУ. В отношении боковой РУ мнения летчиков разделились.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: General Dynamics F-16A/C/E Fighting Falcon - США - 1974
-
Авиация и Время 2014-02 / И.Михелевич - Универсальный солдат. Самолет F/A-18 Hornet
Самолеты-конкуренты YF-16 и YF-17, участвовавшие в тендере ВВС США на легкий истребитель
Другие самолёты на фотографии: General Dynamics F-16A/C/E Fighting Falcon - США - 1974
-
Мировая Авиация 175
YF-17A был облетан в июне и августе 1974 года, а после проигрыша в тендере ВВС США был передан на оценочные испытания ВМС США, которым требовался новый истребитель-бомбардировщик. В конечном итоге на базе Cobra компании "McDonnell Douglas" и "Northrop" создали палубный F/A-18 Hornet, отличавшийся рядом необычных элементов конструкции, включая хвостовое оперение с двумя разваленными килями и крыло с большими наплывами.
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2023-04 / М.Никольский - F-16. Истребитель, о котором сегодня все говорят (2)
Первый опытный YF-17 на испытаниях
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2024-07 / М.Никольский - Рождение F-16 (4)
Опытный истребитель YF-17
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2023-03 / М.Никольский - F-16. Истребитель, о котором сегодня все говорят (1)
Опытный истребитель YF-17
-
Air International 1978-12 / ??? - From Cobra to Hornet... The venomous F-18
Subject of the demonstrations in Canada in connection with the NFA evaluation, this is the second of two YF-17s built originally for the USAF in its LWF programme; the Canadian national insignia are for publicity purposes only and do not indicate that the aircraft is on CAF strength.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1974-08 / News Spotlight
The Northrop YF-17 Cobra first flew on June 9, 1974, from Edwards AFB.
-
Air International 1978-12 / ??? - From Cobra to Hornet... The venomous F-18
During 1976, the first YF-17 underwent an eight-week flight research study at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center.
-
Air Pictorial 1977-08 / J.Cook - Paris Report
Northrop YF-17 01570, acting as the Navy YF-18 Hornet prototype and flown by Hank Chouteau, started with a 60-deg. accelerating climb
-
Air International 1978-12 / ??? - From Cobra to Hornet... The venomous F-18
The two YF-17 prototypes have appeared in several alternative finishes since their first flights, at which time the first was basically natural metal and the second (photo) was in a mottled blue-white sky camouflage.
-
Авиация и Время 2014-02 / И.Михелевич - Универсальный солдат. Самолет F/A-18 Hornet
Опытный истребитель YF-17 в испытательном полете
-
Изд-во Schiffer / S.Markman & B.Holder - One-of-a-kind research aircraft
The YF-17 served as a prototype during competition with the YF-16 in the Air Force Lightweight Fighter competition. The YF-17 aircraft lost that competition, but it would then serve as the testbed for the Navy F/A-18 fighter.
-
Air International 1978-12 / ??? - From Cobra to Hornet... The venomous F-18
The two YF-17 prototypes have appeared in several alternative finishes since their first flights, at which time the first (photo) was basically natural metal and the second was in a mottled blue-white sky camouflage.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1976 / 01 - Aircraft
Northrop YF-17 lightweight fighter (two General Electric YJ101 turbojet engines)
-
Авиация и Время 2014-02 / И.Михелевич - Универсальный солдат. Самолет F/A-18 Hornet
Второй опытный истребитель YF-17
-
Air International 1978-12 / ??? - From Cobra to Hornet... The venomous F-18
After the Northrop YF-17 design had been adopted, as the F-18, by the Navy, the second prototype acquired Navy markings as well as a revised paint scheme.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1976-11 / News Spotlight
Northrop’s YF-17, which put on a spirited performance, is a development aircraft for the US Navy’s F-18, of which a land-based version is mooted.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1977-08 / B.Service - Paris Spotlight
Northrop's YF-17, now serving as the prototype for the US Navy's F-18 Naval Strike Fighter, makes a snappy take-off.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1977-08 / B.Service - Paris Spotlight
This plan view of the Northrop F-18 prototype portrays the leading-edge wing root extensions and the underwing intakes. Sidewinders are carried on the wing tips.
-
Air Pictorial 1976-10 / ??? - Farnborough Report
Northrop YF-17 72-1570 on touch-down with slats and flaps out and a confusion of tails plus dorsal airbrake
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1977-08 / B.Service - Paris Spotlight
A view of the Northrop F-18 prototype which emphasises its twin fins.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1980 / Encyclopedia of Aviation - Aircraft A-Z - v5
Northrop F-18L prototype multi-role land-based fighter, counterpart of the US Navy's McDonnell Douglas Hornet.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1978-04 / News Spotlight
A sidewinder-equipped Northrop YF-17 prototype in Canadian markings in anticipation of the possible order of CF-18Ls for the CAF.
-
Air International 1978-09 / R.Baybrook - Combat Aircraft Spectrum
The Northrop F-18L (represented here by one of the YF-17 prototypes) is a contender for the Canadian Armed Forces New Fighter Aircraft programme. while the F-18 and A-18 versions are being developed by McDonnell Douglas for the US Navy and Marine Corps.
-
Air International 1978-12 / ??? - From Cobra to Hornet... The venomous F-18
Progenitor of the Hornet, this Northrop YF-17 was demonstrated in Canada earlier in 1978 to represent the CF-18L, one of the contenders for the Canadian Armed Forces New Fighter Aircraft programme.
-
Air International 1974-03 / ??? - Northrop's new fighter generation
The fuselage of the first YF-17 is seen after removal from the assembly jig and prior to 'wing mating.
-
Авиация и Время 2014-02 / И.Михелевич - Универсальный солдат. Самолет F/A-18 Hornet
Сборка первого опытного самолета YF-17
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2024-06 / М.Никольский - Рождение F-16 (3)
Модели самолетов по проекту P-300
-
Air Enthusiast 1971-06 / R.Braybrook - The Fight for the skies. Air Superiority /Fighter Spectrum/ (1)
This full-scale mock-up shows salient features of the proposed Northrop P-530 Cobra, including the unusual location of air intakes for the General Electric GE15 engines.
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2024-06 / М.Никольский - Рождение F-16 (3)
Полноразмерный макет истребителя P-530 «Кобра»
-
Мировая Авиация 175
Northrop YF-17 Cobra (1974 год). Самолет создавался в инициативном порядке как Northrop P-600 на базе не пошедшего в серию P.530 (на снимке, 1968 год). Cobra был представлен на тендер ВВС США по программе легкого истребителя (1974 год), но в следующем году проиграл General Dynamics YF-16 Fighting Falcon.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-01 / Airscene
This new photograph of the projected Northrop P-530 Cobra illustrates the fact that, although optimised for the air superiority role, it will carry a substantial ordnance load when operated in its secondary role of close support and interdiction. On a close support mission up to 10,000 lb (4 536 kg) of deliverable weapons may be hung from six wing pylons and one fuselage pylon, and maximum external load of weapons and fuel will be 16,000 lb (7 257 kg).
-
Авиация и Космонавтика 2024-06 / М.Никольский - Рождение F-16 (3)
Регистрационный номер: D-5305 Макет доработанного варианта P-530-5 с нерегулируемыми воздухозаборниками. Внешне точно таким был и проект P-600
-
Авиация и Время 2014-02 / И.Михелевич - Универсальный солдат. Самолет F/A-18 Hornet
Модель многоцелевого истребителя P-530-2
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-10
Продувка модели одного из вариантов «Кобры»
Photo of wind tunnel test model using oil to demonstrate air flow. -
Air International 1974-03 / ??? - Northrop's new fighter generation
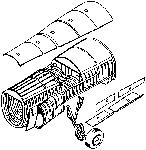
A complete YF-17 model undergoing wind tunnel testing. In addition to testing of the YF-17 configuration itself, the design benefits from earlier development of the P-530 Cobra.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-10
Hooded look gives Cobra its name.
-
Air International 1974-03 / ??? - Northrop's new fighter generation
A mock-up of the YF-17 engine duct, inlet, inlet ramp, and adjacent wing and fuselage surfaces. Prior to first flight, an actual YJ-101 engine was being mated to this mock-up and was to be run to maximum power (including afterburner operation) to demonstrate engine-airframe compatibility.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-08 / ??? - Cobra concept: Recipe for Success?
An impression of the Northrop P-600, two prototypes of which will be evaluated by the USAF.
-
Изд-во Schiffer / S.Markman & B.Holder - One-of-a-kind research aircraft
An artist's concept of the F-18 Hornet fighter that would evolve from the YF-17 testbed prototype.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-08 / ??? - Cobra concept: Recipe for Success?
Northrop P-530 Cobra
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-08 / ??? - Cobra concept: Recipe for Success?
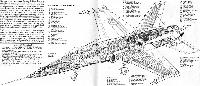
An example of typical Cobra structure is given by this drawing of the centre fuselage section, the production of which would represent nearly 11 per cent of the flyaway cost of the aircraft.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-08 / ??? - Cobra concept: Recipe for Success?
A diagram showing the breakdown of the Cobra airframe into its major components.
-
Air Enthusiast 1971-08 / Airscene
The Northrop P-530 Cobra advanced air superiority fighter, illustrated by the accompanying general arrangement drawing, has been based on F-5 concepts and philosophy but bears no resemblance to the earlier design. Northrop is currently endeavouring to enlist foreign financing for the development of the Cobra which is a purely private venture intended to form the basis of a collaborative manufacturing programme. Including research and development, the Cobra is expected to have a unit price of the order of $3m (?1,25m) and will be powered by two General Electric J101-GE-100 turbojets each having an augmented thrust of approximately 15,000 lb (6 804 kg). Development of the Cobra airframe and systems is expected to cost $100m (?41,6m), Northrop having already spent some $22m (?9,1Im), and it is estimated that the development and flight testing of the J101 engine will cost about $150m (?62,5m.).
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1972 / 07 - Addenda
Northrop P-530 Cobra single-seat combat aircraft
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-08 / ??? - Cobra concept: Recipe for Success?
This general arrangement drawing of the P-530 Cobra, although still provisional, is believed to be the most accurate yet published. It shows a number of significant changes made since the Cobra design was started, including a deeper fuselage, revised air intakes and separate windscreen and cockpit cover. Approximate overall dimensions are span, 35 ft (10,67 m) and length 52 ft (15,85 m).
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-06 / Airscene
This provisional general arrangement drawing illustrates the major external features of the Northrop P-600, two prototypes of which have been ordered for the USAF to define capabilities of the lightweight fighter concept. The P-600 employs most of the aerodynamic features of the projected P-530 Cobra multi-role fighter but weights considerably less with a gross weight of 19,600 lb (8 890 kg).
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1974 / 01 - Aircraft
Northrop YF-17 single-seat lightweight fighter prototype
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1975 / 01 - Aircraft
Northrop YF-17 single-seat lightweight fighter prototype
-
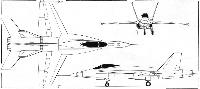
Air International 1974-03 / Plane facts
The latest three-view drawing of the YF-17 shows several recent design changes, including the addition of nose strakes, bell-mouth air intakes and vertical and horizontal tail surfaces of higher aspect ratio than at first planned.
- Фотографии