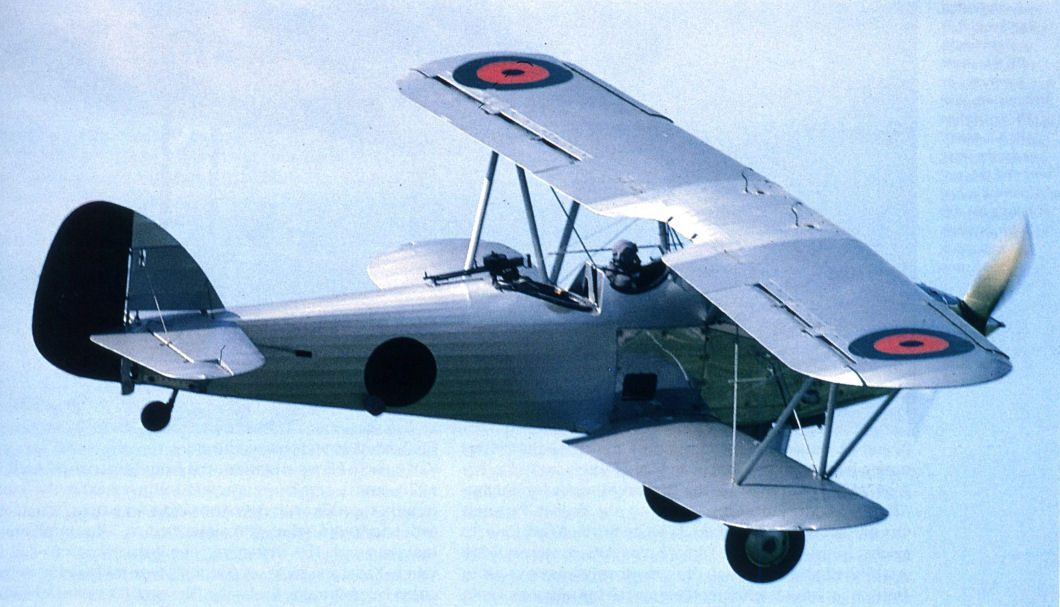
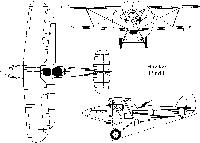
Описание
Страна : Великобритания
Год : 1934
Двухместный легкий бомбардировщик и учебный самолет
Варианты
- Hawker - Hart - 1928 - Великобритания
- Hawker - Osprey - 1930 - Великобритания
- Hawker - Audax - 1931 - Великобритания
- Hawker - Demon - 1932 - Великобритания
- Hawker - Hardy - 1934 - Великобритания
- Hawker - Hind - 1934 - Великобритания
- Hawker - PV.4 - 1934 - Великобритания
- Hawker - Hartbees - 1935 - Великобритания
- Hawker - Hector - 1936 - Великобритания
Hind
Легкий дневной бомбардировщик. Одномоторный цельнометаллический биплан с неубирающимся шасси. Спроектирован в КБ фирмы "Хаукер эйркрафт" под руководством С. Кэмма. Явился развитием типа "Харт". По сравнению с последним, изменили заднюю кабину (по типу самолета "Демон"), ввели хвостовое колесо вместо костыля и модернизировали внутреннее оборудование. Опытный образец "Хинда" совершил первый полет 4 сентября 1935 г. Серийное производство было развернуто в конце 1935 г. на заводе "Хаукер" в Лэнгли. Всего было изготовлено 507 экз. всех модификаций (включая 20 учебных).
Двигатель "Кестрел" V (на большинстве машин), "Кестрел" VDR (на учебно-тренировочных), "Меркьюри" VIII (на экспортных для Ирана). Экипаж самолета - 2 чел. Вооружение 2x7,69, бомбы до 227 кг.
Самолет состоял на вооружении в Великобритании с декабря 1935 г., в Португалии - с июня 1937 г., Югославии и Новой Зеландии - с 1937 г., Латвии - с января 1938 г., в Иране и Афганистане - с апреля 1938 г., в Ирландии - с 1939 г.
Выпускались следующие основные модификации:
- "Хинд" I с мотором "Кестрел" V, основной боевой вариант, на его базе изготовлялись учебно-тренировочные машины с мотором "Кестрел" VDR и двойным управлением;
- "Хинд" с мотором "Кестрел" V/VDR и увеличенным маслорадиатором, экспортный вариант для Афганистана;
- "Хинд" с мотором "Меркьюри" VIII - экспортный вариант для Ирана.
Производство прекращено в 1938 г.
В британских Королевских ВВС "Хинд"" начал сниматься с вооружения боевых частей с середины 1938 г. Последние строевые эскадрильи сдали их в январе 1939 г., но самолет продолжал использоваться в учебных и вспомогательных подразделениях. Эти машины служили как самолеты связи в британском экспедиционном корпусе во Франции в 1939 г. Как учебные самолеты и буксировщики мишеней "хинды" эксплуатировались в Англии до конца 1942 г.
Югославские машины совершили фактически всего один боевой вылет против немцев. 8 мая 1941 г. они совместно с "бленхеймами" бомбили колонну танков к югу от Куманова и были сбиты немецкими истребителями. Самолеты иранских ВВС участвовали в боевых действиях против английских войск во время оккупации южной части Ирана в августе 1941 г. "Хинд" окончательно сняли с вооружения в Великобритании в 1943 г., в Португалии и Ирландии - в 1944г., в Иране - в 1948 г., в Афганистане - в 1949 г.
"Хинд" I||
Размах:||11,35 м
Длина:||8,85 м
Моторы, количество х мощность:||1 x 640 л.с.
Взлетная масса, максимальная:||2440 кг
Максимальная скорость:||300 км/ч
Практический потолок:||8000 м
Дальность:||690 км
Описание:
- Hind
- Hawker Hind
Фотографии
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: K5372 Hind K5372 of 139 Sqn
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: K5398 Hind K5398 of 34 Sqn
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: K6654 Hind K6654 of 610 Sqn
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: K6812 Hind K6812 of 50 Sqn
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: L7188 Hind L7188 of 103 Sqn
-
Мировая Авиация 206
Регистрационный номер: L7189 В ноябре 1941 года этот учебный Hind, L7189, имевший дублированное управление, принадлежал 1-й летной школе. К следующему январю самолет сняли с летной эксплуатации и передали в другое учебное подразделение. Самолет - из последней партии в 70 машин, построенных компанией "Hawker" в 1937 году.
-
Air Enthusiast 2003-05 / L.Andersson - Turbulent origins
The Shuttleworth Collection's Hind flew initially with Afghan colours (here in 1983). It later adopted RAF markings.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1984-05
The Shuttleworth Collection's Afghan Hawker Hind. Delivered to the Royal Afghanistan Air Force in 1937, where it remained in service until 1956, this aircraft returned to this country in 1971 and flew again ten years later. How nice it would be to see the aircraft painted up as an RAF Hind!
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1999-12 / D.Mackay - Flying the golden Hind /Pilot report/
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] The Hind displays its four underwing 125lb dummy bombs as pilot Gordon McClymont eases it closer to the camera aircraft.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1999-12 / D.Mackay - Flying the golden Hind /Pilot report/
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] Resplendent in 15 Sqn markings, the Hind cruises above the clouds during a late summer afternoon in September this year. Gordon McClymont is at the controls.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1993-02
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] -
Aeroplane Monthly 1999-12 / D.Mackay - Flying the golden Hind /Pilot report/
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] Cockpit close-up: flying the Hawker Hind
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1999-12 / D.Mackay - Flying the golden Hind /Pilot report/
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] Every stitch of the fabric covering and every reflection in the polished metal cowling is picked up in this dramatic close-up.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1999-12 / D.Mackay - Flying the golden Hind /Pilot report/
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] The clean lines of the Hind’s fuselage are well displayed as Dodge Bailey peels away from the camera in July 1996.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1999-12 / D.Mackay - Flying the golden Hind /Pilot report/
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] The Hind was a modern design, its fabric-covered, tubular Warren-girder primary fuselage structure having originated with the Hawker Hart. Here, the fabric may be seen bulging between the wing ribs.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 2001-04 / Airshows & Museums Guide
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] Shuttleworth’s splendid Hawker Hind “K5154” ("K5414" ???) was recovered from Afghanistan in the 1970s.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1998-12 / T.Harmsworth - Airshows: boom or bust? /The airshow business/
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] For many enthusiasts the quintessential English airshow: the Shuttleworth Collection at Old Warden. Its shows have a distinctive, timeless character reinforced by its setting on an intimate grass aerodrome. This typical view shows the Collection’s Comet racer taxying past the Magister, Hind and Hucks Starter in May 1995.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: De Havilland Comet / D.H.88 - Великобритания - 1934Miles Magister / M.14 - Великобритания - 1937
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1999-12 / D.Mackay - Flying the golden Hind /Pilot report/
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] In the rear cockpit a single Lewis machine-gun is mounted on a No 15 ring. During displays the gun is latched in place.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1999-12 / D.Mackay - Flying the golden Hind /Pilot report/
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] Mechanised starting. 1. Careful positioning is required in order to engage the propeller-boss driving-dog. 2. Shuttleworth chief engineer Chris Morris locates the starting shaft into the propeller boss. 3. Connection complete. 4. The Hucks operator turns the engine over a few times while the pilot operates the priming pump. 5. With everyone clear of the propeller, the throttle is opened and the Hucks turns the engine. Immediately the Kestrel bursts into life, and the starter disengages.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1990-05 / Personal album. Military
Регистрационный номер: K4636 [13] Hawker Audax (Hind ???) K4636 again. Following trials with the A&AEE, it joined the Station Flight at RAF Northolt before being shipped to South Africa for service with the SAAF.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1990-05 / Personal album. Military
Регистрационный номер: K4636 [13] Mr Kirkby "winding up" the Rolls-Royce Kestrel IB engine of Hawker Audax (Hind ???) K4636. This particular Audax was converted into a trainer by General Aircraft Ltd. Designed initially for army co-operation work, the Audax - a Hart variant - entered service in that capacity in February 1932. Its long exhaust pipe and message-collecting hook identified the Audax in this role.
-
Air Pictorial 1977-06 / J.Holmes - The Hart Family (3)
Регистрационный номер: K4636 [13] The first production Hind, K4636, which flew on 4th September 1935
-
Flight 1935-09 / Flight
DEADLIER THAN THE MALE. Another remarkable "close-up" of the Hawker Hind. A very large batch of these machines is being produced by the Hawker Company. The fully supercharged Kestrel V will come as a treat to pilots who have been flying Harts with naturally aspirated engines.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1984-07 / A.Lumsden, T.Heffernan - Probe Probare (5)
Регистрационный номер: K4636 [13] The Hind two-seat bomber and general purpose machine was powered by the 640 h.p. Rolls-Royce Kestrel V, had a cutaway rear gunner's cockpit and sported a tailwheel.
-
Flight 1938-05 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: K4636 [13] HAWKER HIND: Bomber (Kestrel V engine - 640 h.p. at 14,000ft.); span, 37ft. 3in.; gross weight, 4,958 lb.; max. speed, 186 m.p.h. at 16,400ft.
-
Flight 1936-11 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: K4636 [13] A typical Hawker two-seater biplane: the Hind light bomber (R-R. Kestrel V) as used by the R.A.F.
-
Flight 1935-12 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: K4636 [13] With the 600 h.p. Kestrel V the Hawker Hind does about 200 m.p.h.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1992-01 / J.Fozard - Camm's engine legacy
Регистрационный номер: K4636 [13] A Rolls-Royce Kestrel V engine assists Hawker Hind K4636 in its downward path over Brooklands in September 1935.
-
Мировая Авиация 206
Регистрационный номер: K4636 [13] Hind - наследник Hart. В 1935 году Министерство авиации подготовило требования к самолету, который должен был временно заменить Hart до поступления в войска более современных бомбардировщиков-монопланов. Однако достоинства Hart были столь велики, что в компании "Hawker" решили просто модернизировать его - новый вариант получил обозначение Hind (на фото). На самолет установили более мощный двигатель Kestrel V, новую заднюю кабину, улучшили возможности наблюдателя/стрелка по прицельному бомбометанию и заменили хвостовое колесо на костыль. К весне 1937 года более 300 бомбардировщиков Hind поступили на вооружение 20 эскадрилий Бомбардировочного командования. Но уже к осени того же года в войска стали поступать более современные самолеты, и Hind стали постепенно снимать с вооружения строевых частей. Кроме того, потребность в учебных машинах побудила военных в 1938 году выдать заказ компании "General Aircraft" на постройку 124 самолетов Hind с дублированным управлением.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1980-10
Регистрационный номер: K4636 [13] THE FEMALE OF THE SPECIES. This fine photograph of the first production Hawker Hind light bomber being flown by Mr. M. Summers was secured by Flight's chief photographer from the Hart "MR," with Mr. J. S. Hindmarsh as pilot. The Hind, a development of the Hart, is fitted with ths fully supercharged Kestrel V engine of 600/640 h.p. (700 h.p. for takeoff) and does nearly 200 m.p.h. with full military load at 14,000 ft. Note the Demon-type rear cockpit and the tail wheel.
The first production Hawker Hind, K4636 -
Aeroplane Monthly 1976-06 / ??? - Beautiful Biplanes
Регистрационный номер: K4636 [13] -
Flight 1935-10 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: K4636 [13] Going Down: An R.A.F. Hind (Kestrel V) light bomber demonstrate how dive bombers enter their dives.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: K4636 [13] An impressive plan view of K4636, the first production Hind, taken during a sortie from Brooklands, emphasizes the contrast between the swept upper wing and the straight lower wing. Note also the underwing bomb carriers.
-
Flight 1936-06 / Flight
The Hawker Hind light bomber (Kestrel V, 600 h.p.).
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: K4644 34 Sqn Hind K4644 with its engine cowlings removed for maintenance. The squadron number, in the Flight colour, is positioned well ahead of the fuselage roundel.
-
Flight 1936-08 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: K4648 OPERATIONAL HEIGHT. Hawker Hind light bombers are now well established as Service equipment. Their engines - Rolls-Royce Kestrel Vs, which give a maximum of 640 at 14,000 ft. - permit them to operate efficiently at high altitudes where they can attain speeds up to 200 m.p.h. This "shot," secured during the recent exercises, depicts Hinds of No. 104 Squadron. Note, incidentally, the new "kidney" type exhausts and the "cut-away" gunners cockpits as on the Demon two-seater fighter.
-
Flight 1938-05 / Flight
Hawker Hinds of No. 50 (B.) Squadron, Waddington, climbing in formation. The leader is in communication with the other pilots by R/T.
-
Air Pictorial 1977-06 / J.Holmes - The Hart Family (3)
Регистрационный номер: K5373 First squadron to receive Hinds was No. 21 at Bircham Newton in December 1935 - K5373 illustrated
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: K5401 44 Squadron Hinds carried the squadron number in the appropriate Flight colour ahead of the roundel. Visible here is the window by the bomb-aiming position.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1984-08 / P.Jarrett - Grapevine
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] As reported in our June issue, Shuttleworth's Hawker Hind now wears the colours of XV Squadron, RAF, and carries the serial number K5414. Our photograph shows the Hind returning from RAF Mildenhall on June 10 with John Lewis piloting.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1984-09
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] The first colour air-to-air photograph published of Shuttleworth's Hawker Hind resplendent in its new XV Squadron markings. The scheme was first seen in public at RAF Mildenhall during the weekend of June 9-10 this year.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1990-12 / M.Oakey - Grapevine
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] Unique formation No 1: the Shuttleworth Collection's Spitfire, Gladiator and Hind fly past during the Richard Ormonde Shuttleworth Commemorative Pageant at Old Warden on October 7, 1990.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Gloster Gladiator - Великобритания - 1934Supermarine Spitfire Mk.V - Великобритания - 1941
-
Air Enthusiast 1996-11 / A.Thomas - Over All Things Everywhere
Регистрационный номер: K5416 On re-forming in Bomber Command, 82 Squadron flew Hind light bombers such as K5416, being flown by Pilot Officer Atkinson in 1937.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1980 / Encyclopedia of Aviation - Aircraft A-Z - v3
Регистрационный номер: K5420, K5423 Hawker Hinds.
-
Air Pictorial 1977-06 / J.Holmes - The Hart Family (3)
Регистрационный номер: K5426 Bombing practice by No. 40 Squadron Hind K5426
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: K5443 Hind K5443, from the second production batch, displays the markings of 49 Sqn. The squadron number was carried well forward of the fuselage roundel, and the squadron’s greyhound badge was set in a grenade frame on the fin.
-
Air-Britain Aeromilitaria 1982-03 / Royal Air Force January 1939
Регистрационный номер: K5475 Hind of No.4 E & R FTS
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: K5481, K5486, L7186, L7190, L7193 A Hind quintet from 18 Sqn. K5486 and K5481 have the unit’s Pegasus emblem on their fins, but L7186, L7190 and L7193 lack this adornment.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1990-11 / Personal album. Military
Регистрационный номер: K5502 Hawker Hind K5502 was delivered to the RAF in late 1936. After initial service with 602 Squadron, K5502 passed to 35 ERFTS, 5 FTS, 15 FTS and in December 1940 was shipped to the Royal New Zealand Air Force. The Hind two-seat light bomber first went into RAF service with 21 Squadron, and in 1935 had had the distinction of being the RAF’s last biplane light bomber. It remained in first-line squadron use until early 1939.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1990-11 / Personal album. Military
Регистрационный номер: K5514 Hawker Hind K5514 was delivered to the RAF in 1936 and during its short life served only with 104 Sqn, based at Abingdon and Hucknall. On April 9, 1937 K5514 crashed while taking off from Hucknall. The Hind general purpose two-seat light bomber was powered by a 640 h.p. Rolls-Royce Kestrel V engine and differed from the Hart by way of the cutaway gunner's cockpit and the tail wheel.
-
Air Enthusiast 2003-05 / L.Andersson - Turbulent origins
Регистрационный номер: K5554 K5554 was one of the 20 second-hand Hawker Hinds that were acquired in 1939.
-
Air Pictorial 1977-06 / J.Holmes - The Hart Family (3)
Регистрационный номер: K5382, K5442, K6644 Hinds K6644, K5382 and K5442 of No. 49 Squadron during 1937 Air Defence Exercises. Greyhound on fin comes from No. 49's badge
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-02 / Personal album. Military
Регистрационный номер: K6680 Hawker Hind K6680 of 103 Squadron, based at RAF Andover and later at RAF Usworth. The squadron had Hinds on strength from August 1936 until October 1940. This particular Hind passed to 26 ERFTS, RAFC and 15 FTS before being shipped to the South African Air Force in October 1941.
-
Air Pictorial 1977-06 / J.Holmes - The Hart Family (3)
Регистрационный номер: K6689 K6689, a late series Hind
-
Flight 1937-09 / Flight Advertisements
Регистрационный номер: K6734 -
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: K6785 Hind K6785 of 28 Elementary Reserve Flying Training School at Desford, Leicestershire, prepares to takeoff. The casual attire of the gentleman about to enter the gunner’s cockpit seems singularly inappropriate for an RAF unit.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1979-03 / J.Corlett - One good turn
Регистрационный номер: K6818 Двигатель "Хинда" можно было завести ручкой (с помощью инерционного стартера)
“Winding up the elastic” - hand starting the Kestrel X engine of Hawker Hind K6818. Note the unstable position of the “erks” -
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
Регистрационный номер: K6845, K6848 Hinds K6845 and K6848 of 609 (West Riding) Sqn, based at Yeadon, undergo maintenance. Note the unusual positioning of the squadron number under the cockpit.
-
Flight 1939-10 / Flight
"Formidable-looking British fighter ’planes flying in perfect formation on patrol. These speedy machines are the equal of the vessels of their type in any country." Believe it or not, that was the caption supplied with this photograph, an it had been passed by Censor. Apart from tending to make the good old Hind look ridiculous, it is scarcely good propaganda for neutral countries, which are now being flooded with pictures of modern German military aircraft types.
-
Flight 1938-03 / Flight
BELFAST OPENING: Hawker Hind light bombers of No. 502 (Ulster) (Bomber) Squadron in their demonstration of formation flying at the opening last Wednesday, by Mrs. Neville Chamberlain, of the Belfast Harbour Airport. The airport adjoins the Short and Harland factory, so presumably will be used for the testing of the Hereford bombers now under construction.
-
Мировая Авиация 152
К началу Второй мировой войны все сохранившиеся Hind несли камуфляж цветов Dark Earth/Dark Green.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1984-08 / D.Higgs - Go Shoot Yourself!
Shuttleworth's Hawker Hind: a view from the tailfin. Remote-controlled cameras make this kind of shot possible without upsetting the photographer, the pilot or the center of gravity.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1984-08 / D.Higgs - Go Shoot Yourself!
Two more views of the Shuttleworth Hind were taken during a loop.
-
Flight 1938-06 / Flight
The modification of a Hawker Hind for high-speed parachute dropping at Henlow. Speeds of about 320 m.p.h are attained before release of the dummy. A static line is fitted to ensure clearing the structure. This Hind gave a demonstration on Empire Air Day
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
The observer/gunner of a 98 Squadron Hind describes the intricacies of one of the tools of his trade, the 0-303in Lewis machine gun, to some budding aircrew.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-08 / O.Thetford - Hawker Hart and Hind /By day and by night/ (2)
A pre-flight check of the four 20lb bombs on their carrier.
-
Air Enthusiast 1971-06 / ??? - The RAF museum takes shape /Veteran & Vintage/
Among the Hawker biplanes included in the Camm Memorial Hall at Hendon will be this Hind, returned from Afghanistan and restored in full Royal Afghan Air Force markings.
-
Flight 1937-06 / Flight
In the large photograph details of composite cooling system, including the pipe leading to the specially faired strut, can be seen. The machine in the latter case is a Hawker Hind
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1981-10 / News Spotlight on the Shuttleworth Hawker Hind
The Rolls-Royce Kestrel I was originally supplied to the RAAF from Brooklands before the war.
-
Flight 1936-07 / Flight
The scene at Mildenhall on the arrival of the King, with a background of Hinds and Heyfords.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: De Havilland Dragon Rapide / Dominie / D.H.89 - Великобритания - 1934Handley Page Heyford / H.P.38 / H.P.50 - Великобритания - 1930
-
Flight 1939-01 / Flight
R.A.F.V.R.: Lt. Col. (Hon. Wing. Cdr.) G. N. Buckland (right) in charge of No. 34 elementary flying school of the Royal Air Force Volunteer Reserve, newly opened at Southend and operated by Air Hire, Ltd. With him is Flt. Lt. L. P. Rowley, the chief instructor. The aircraft is a Hind Trainer.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1989-03 / M.Oakey - Grapevine
Регистрационный номер: L7180 The CNAM's Hawker Hind L7180, beautifully restored by George Neal.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1979-07 / Hooton Park /Gone but not forgotten/ (3)
Регистрационный номер: L7227 Hawker Hind Trainer L7227 of 610(B) Squadron in 1938.
-
Air Pictorial 1977-06 / J.Holmes - The Hart Family (3)
Регистрационный номер: L7226 Yellow-painted dual-control Hind Trainer L7226 was one of 124 converted from bombers by General Aircraft Ltd.
-
Flight 1938-06 / Flight
Lighter-and-heavier-than-air Day in the big hangar at Cardington. In this non-stop variety picture are barrage balloons, a Blenheim and a Battle (left), a new Hind Trainer (foreground), Hector, Shark, Swordfish and Cloud (right), not to mention other less discernible aircraft and a goodly proportion of the population of Bedfordshire.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Blackburn Shark / B-6 - Великобритания - 1933Bristol Blenheim - Великобритания - 1936Fairey Battle - Великобритания - 1936Fairey Swordfish - Великобритания - 1934Hawker Hector - Великобритания - 1936Saunders-Roe Cloud / A.19 - Великобритания - 1930
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1994-12 / G.Wansbrough-White - What's in a name? (2)
THE STAGE SET: This aerial photograph of the Royal Air Force Display machines assembled in the operational park at Hendon forms a fitting introduction to the pictures, in the ensuing pages, of the Display in progress. There are eight monoplanes in the assembly - Ansons (third row) and Clouds (fifth).
Line-up of about 130 1936 RAF Display participants - all biplanes except for the Ansons and Saro Cloud amphibians.
The stage is set for the 1936 RAF Display at Hendon. The monoplanes (Ansons and Saro Clouds) are totally outnumbered by the biplanes including Heyfords, Bulldogs, Gauntlets, Fairey IIIFs, Harts, Hinds, Tiger Moth, Overstrands etc, etc. This entire area has since disappeared beneath a sea of bricks and concrete.Другие самолёты на фотографии: Avro Anson / Type 652 - Великобритания - 1935Boulton Paul Overstrand / P.75 - Великобритания - 1933Bristol Bulldog - Великобритания - 1927De Havilland Tiger Moth / D.H.82 - Великобритания - 1931Fairey Fairey IIIF - Великобритания - 1926Gloster Gauntlet - Великобритания - 1929Handley Page Heyford / H.P.38 / H.P.50 - Великобритания - 1930Hawker Hart - Великобритания - 1928Saunders-Roe Cloud / A.19 - Великобритания - 1930
-
Flight 1937-07 / Flight
The view shows a Portuguese Hind just after taking off from Brooklands. This model has a Kestrel V engine and is similar to the machines which equip several R.A.F. Squadrons.
-
Flight 1937-09 / Flight Advertisements
HIGH PERFORMANCE: One of the Hawker Hind day Bombers (Kestrel V. Engine) supplied to the Portuguese Air Force.
-
Мировая Авиация 206
После появления в 1935 году первых серийных Hind швейцарское правительство заказало один самолет для оценки. Заказа от Швейцарии не последовало, но в следующем году Португалия приобрела 4 самолета, оснащенных двигателями Kestrel V, - два бомбардировщика и два учебных с дублированным управлением (на фото).
-
Air Pictorial 1977-06 / J.Holmes - The Hart Family (3)
One of four Kestrel V-powered Hinds built for the Portuguese Air Force, shown carrying two 230-lb. bombs
-
Air Enthusiast 2003-07 / Round-Out
Afghan Hawker Hind No.6 taken at Peshawar in January 1947. Note the overwing stripes and what is believed to be a unit marking on the fuselage - see the detail view.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1999-12 / D.Mackay - Flying the golden Hind /Pilot report/
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] Shuttleworth’s Hind before its return to England. The aircraft had been stored at Bagram, a military airfield north of Kabul.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1981-05 / News Spotlight
The Shuttleworth Collection’s ex-Afghan Air Force Hawker Hind nears the end of its ten year restoration programme. At the time of press its 600 h.p. Rolls-Royce Kestrel was awaiting its first run since the early 1950s. The Hind should be flying during the season.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1980-07 / News Spotlight
On May 25, 1980 Shuttleworth's Hawker Hind came out of doors at Old Warden for the first time in ten years. Engine runs should begin late summer.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1981-10 / News Spotlight on the Shuttleworth Hawker Hind
Returning from its second flight, note the fixed Vickers gun.
Dicky Martin taxies in after the second flight was curtailed by a dicky magneto. -
Aeroplane Monthly 1981-10 / News Spotlight on the Shuttleworth Hawker Hind
The Hind before flight testing, complete with rear Lewis gun.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1981-10 / News Spotlight on the Shuttleworth Hawker Hind
Unsticking for its first flight.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1981-10 / News Spotlight on the Shuttleworth Hawker Hind
The Hind lifts off from Old Warden on its first flight for 26yr on Monday, August 17, 1981.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1982-01 / Grapevine
The Afghan Hind flying with the rear seat occupied.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1983-06 / T.Dudgeon - The roof of the world
The Shuttleworth Trusts's recently restored Afghan Hawker Hind.
-
Моделист-Конструктор Ближние разведчики, корректировщики и штурмовики Второй мировой войны
"Хинд" I с мотором "Кестрел" в полете
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1984-07 / A.Lumsden, T.Heffernan - Probe Probare (5)
A last look at Shuttleworth's Hawker Hind in its Afghan colours. Its debut in its new 15 Sqn RAF scheme will be at Mildenhall on June 9-10, 1984.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1981-10 / News Spotlight on the Shuttleworth Hawker Hind
“Dicky” Martin hands down his test notes after the second flight, during which low speed handling was investigated.
-
Мировая Авиация 206
После появления в 1935 году первых серийных Hind швейцарское правительство заказало один самолет для оценки (на фото). Заказа от Швейцарии не последовало.
-
Air Pictorial 1977-06 / J.Holmes - The Hart Family (3)
Регистрационный номер: HB-HAL The sole Swiss Hind, HB-HAL, which was acquired in 1936 for evaluation by the Swiss Air Force. Powered by a Kestrel V, it was similar to R.A.F. machines but did not find favour
-
Flight 1937-07 / Flight
THE view shows a Hawker Hind destined for Yugoslavia. This machine differs from the standard R.A.F. Hind in that it is fitted with the Rolls-Royce Kestrel XVI (690 h.p. at 11,000 ft.) which is provided with a central air intake forward of the radiator and a cylindrical oil cooler mounted in a trough on the starboard side of the cowling.
-
Flight 1937-09 / Flight Advertisements
UNDERGOING TESTS. The first Hawker Hind for the Royal Jugo-Slav Air Force (Kestrel XVI Engine.)
-
Air Pictorial 1977-06 / J.Holmes - The Hart Family (3)
Last of three Hinds for the Yugoslav A.F., with Gnome-Rhone K-9 Mistral engine
-
Air Pictorial 1977-06 / J.Holmes - The Hart Family (3)
Last of three Bristol Mercury IX-powered Hind dual-control trainers produced for the Latvian Air Force, serial 178
Хоукер «Хинд» английского производства -
Aeroplane Monthly 1985-06 / P.Capon - Capon's Corner
Hawker "Latvian" Hind 117, powered by a Bristol Mercury IX engine, photographed at Hawker's flight sheds at Brooklands in May 1938. The chap in the centre of the group of three is Hawker test pilot R. C. “Dick" Reynell who was later killed during the Battle of Britain. The two other people standing with him were Latvian acceptance personnel.
-
Авиация и Время 1999-05 / А.Котлобовский - Иранский эпизод /Аэроархив/
Разведчик-легкий бомбардировщик Хаукер "Хинд" ВВС Ирана
-
Air Enthusiast 2000-11 / L.Andersson - Iranian Eagles
One of the last British-built Hinds, 631, probably in the UK before delivery to Iran
-
Моделист-Конструктор Ближние разведчики, корректировщики и штурмовики Второй мировой войны
"Хинд" с мотором "Меркьюри" VIII для Ирана на заводском аэродроме в Англии
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1985-06 / P.Capon - Capon's Corner
A Hawker "Persian” Hind.
-
Air Enthusiast 2000-11 / L.Andersson - Iranian Eagles
The first of 35 Hawker Hinds, 601, arrived in the autumn of 1938.
-
Air Pictorial 1977-06 / J.Holmes - The Hart Family (3)
The first of thirty-five Persian (Iranian) Hinds, serial 601, seen at Brooklands where it made its first flight on 28th April 1938. This version was powered by the Bristol Mercury VIII. Several Persian Hinds were still flying in the late 1940s
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1999-12 / D.Mackay - Flying the golden Hind /Pilot report/
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] Hinds were renowned for their roominess, but the instrument panel and pilot’s controls reveal the typically haphazard layout of an inter-war British cockpit.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1999-12 / D.Mackay - Flying the golden Hind /Pilot report/
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] Dave Mackay flies the Hind back to Old Warden, having just participated in the 1998 International Air Tattoo at Fairford, Gloucestershire.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1999-12 / D.Mackay - Flying the golden Hind /Pilot report/
Регистрационный номер: K5414 [18] The Hind is loaded at Kabul into one of Ford’s latest trucks for its return to the UK in 1970.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1979-04 / News Spotlight
Other Shuttleworth aircraft showing the results of much painstaking effort is the ex-Afghan Air Force Hawker Hind, which is now nearing completion after ten years in the workshops.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1982-04 / R.Cooling - Bravo Juliet
Регистрационный номер: K6779 Two Brough B-2s, their upper fuselage surfaces camouflaged, with Hawker Hind K6779 on its nose in the background.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Blackburn B-2 - Великобритания - 1931
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1989-05 / Personal album. Military
Регистрационный номер: K5510 Hawker Hind K5510 was part of a batch of 193 delivered to the RAF between January and August 1936. It was delivered to 602 Squadron - note the fuselage code - and was lost following an accident at Rochford on July 27, 1937 while flying at summer camp. The Hind struck some telephone wires whilst landing - the incident is depicted here.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1979-04 / Personal album
This training accident involving a Hawker Hind (left) and Hart 397/14 of the SAAF occurred at Watercloof in February 1942. The pupil pilot in the Hind (distinguished by its cut-away gunner’s cockpit) had to pay £120, had a week's pay stopped and was awarded 14 days CB. 397 was one of a batch of 100 ex-RAF Harts serial led 301-400, and the Hind was probably from the 101-199 serial batch, again ex-RAF.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Hawker Hart - Великобритания - 1928
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1984-08 / Personal album
Регистрационный номер: K5458 Hawker Hind K5458 of 211 Squadron is righted at RAF Ismailia in December 1938. K5458 previously flew with 57 Squadron and was struck off RAF charge in December 1939.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1995-12 / Skywriters
Регистрационный номер: K5472 Mr Simmons’s photograph of 18 Sqn Hawker Hind K5472 taken at RAF Upper Heyford following a take-off crash on March 22, 1937.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1999-12 / D.Mackay - Flying the golden Hind /Pilot report/
Two Hinds lay derelict in Afghanistan. Located ahead of the second wreck is a Rolls-Royce Kestrel powerplant.
Тип фотографий
- Все фото (126)
- Боковые проекции (6)
- Цветные фото (13)
- Ч/б фото (95)
- Кабина (2)
- Реставрация (2)
- Обломки (6)
- Схемы, чертежи (2)