Варианты
- Junkers - Ju.86 - 1934 - Германия
- Junkers - Ju.86P/R - 1940 - Германия
Ju.86
Средний бомбардировщик, двухмоторный цельнометаллический моноплан с двухкилевым оперением и убирающимся шасси с хвостовым колесом. Экипаж 4 человека. Спроектирован в КБ фирмы "Юнкерс флюгцойг унд моторенверке" под руководством Э.Цинделя. Первый полет опытный образец Ju 86а совершил 4 ноября 1934 г. Серийное производство - с февраля 1936 г.
Выпускался на заводах "Юнкерс" в Дессау, "Хеншель флюгцойгверке" в Шенефельде. По лицензии изготовлялся на заводе SAAB в Трольгаттане (Швеция) как B3A/B. Выпущено свыше 500 экз. (вместе с пассажирскими вариантами, но без выпуска в Швеции). Ju 86 состоял на вооружении в Германии с весны 1936 г., в Швеции и ЮАС - с 1939 г., а также в Венгрии, Португалии и Чили.
Основные серийные модификации:
- Ju 86A с моторами Jumo 205, вооружение 3x7,9;
- Ju 86K, экспортный вариант Ju 86A, выпускался с различными моторами - "Хорнет", "Пегасус", "Гном-Рон";
- Ju 86Z, гражданский экспортный вариант, самолеты серии Z-7 переделывались в ЮАС в бомбардировщики с вооружением 1x7,69 и наружной подвеской бомб;
- Ju 86D, развитие Ju 86A с измененной хвостовой частью и увеличенным запасом горючего;
- Ju 86E, аналог Ju 86D с моторами BMW 132F или N;
- Ju 86G, аналог Ju 86E с новой носовой частью;
- Ju 86P, высотный бомбардировщик с моторами Jumo 205 и гермокабиной;
- Ju 86R, высотный разведчик-бомбардировщик с моторами Jumo 207B-3, гермокабиной, крылом увеличенного размаха.
Первое боевое применение - в Испании в конце 1937 г. Использовался во время вторжения в Польшу. С сентября 1939 г. постепенно переводился в учебные и транспортные части, но в марте 1943 г. вновь привлекался к операциям против партизан на Балканах, в 1943 - 1944 гг. - в Белоруссии. В сентябре 1943 г. недолго использовался на Восточном фронте как ночной бомбардировщик. Самолеты модификаций Р и R применялись в основном как разведчики. Венгерские Ju 86K воевали против СССР в 1941 - 1943 гг. Южноафриканские Ju 86Z-7 применялись как дневные и ночные бомбардировщики в Восточной Африке в 1940 - 1942гг. против итальянцев.
Ju 86 был снят с вооружения в ЮАС - в сентябре 1942 г., в Германии и Венгрии - летом 1944 г., в Швеции - в 1947 г.
Ju 86D-1||
Размах:||22,48 м
Длина:||17,88 м
Моторы, количество х мощность:||2x600 л.с.
Взлетная масса, максимальная:||8000 кг
Максимальная скорость:||323 км/ч
Практический потолок:||5900 м
Дальность:||1480 км
Описание:
- Ju.86
- Junkers Ju 86
- Flight, June 1936
JUNKERS' NEW "TWIN"
Фотографии
-
Мировая Авиация 113
Этот Junkers Ju 86D-1 принадлежал Kampfgeschwader 254, в сентябре 1937 года базировавшейся в Эшвеге. Позднее, после начала войны, опознавательные знаки на Ju 86 сделали менее яркими.
-
Мировая Авиация 90
Junkers Ju 86D-1. Бомбардировщик Fumo 2 был одним из пяти Junkers Ju 86D-1, летавших в группе J 88 в конце 1937 года. В боях над Испанией этот бомбардировщик зарекомендовал себя не очень хорошо из-за своих ненадежных дизельных моторов Jumo 205.
-
АэроХобби 1994-04 / А.Котлобовский - В тени Люфтваффе (Венгерские ВВС на Восточном фронте в 1941г.) /Аэроархив/ (1)
Junkers Ju-86K, борт B.322 из 4/3 эскадрильи "Шарга Вихар", был выведен из строя 3.07.1941г. после вынужденной посадки
-
Мировая Авиация 162
Показан Ju 86K-2 с двигателями Gnome-Rhone из 4-го бомбардировочного полка ВВС Венгрии, воевавшего в составе германского IV Воздушного флота на территории СССР весной 1942 года.
-
Мировая Авиация 113
С 1938 года Ju 86 выпускался по лицензии шведской фирмой "Saab" под обозначением B3C/Ju 86K-13. К сентябрю 1940 года построили только 16 самолетов, в дополнение к которым еще 40 закупили в Германии. В число машин германской постройки входили три B3 (эквивалент Ju 86K-1), 35 B3A (K-4) и два B3B (K-5). Несколько B3/3A/3B переделали в торпедоносцы, 15 B3A/3B - в транспортные B3C-2 (10 пассажиров) и все 16 B3C (на рисунке) - в транспортные B3D. Эти самолеты также использовались для ведения радиотехнической разведки и прослужили в Швеции до конца 1950-х годов.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-12 / J.Stroud - Wings of Peace
Регистрационный номер: D-AREV [3] The Ju 86 V4 D-AREV, one of the prototypes of the commercial version, in DLH service. The nacelle shape differed from that of the production Ju 86B-0 with Jumo engines.
D-AREV Brocken, the second prototype Ju 86 transport, with straight-tapered wing and original inclined radiators, at Tempelhof during its time with Lufthansa. -
Air Enthusiast 1972-01 / ??? - The airliner that went to war
A Junkers Ju 86B-0 of DLH at Berlin Airport, parked behind a second aircraft of the same type.
-
Flight 1936-05 / Flight
In the German hall The machine in the foreground is the B.F.W. Messerschmitt 108 B, and behind it is the Junkers Ju.86, with two Jumo diesel engines.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Messerschmitt Bf.108 Taifun - Германия - 1934
-
Flight 1937-05 / Flight
This view of a Junkers Ju.86 shows the clean installation of its Jumo 205 Diesels.
-
Flight 1938-11 / Flight
WORKS FERRY: This diesel-engined Ju.86 seen at Croydon recently is the property of Junkers Flugzeugwerke and is used for customary business travels by the staff - and, in particular, by the managing director.
-
Flight 1939-11 / Flight
The installation of a Jumo 205 diesel in a Junkers Ju 86. The airscrew is a V.D.M. electrically operated type.
-
Flight 1939-07 / Flight
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Focke-Wulf FW.200 Condor - Германия - 1937Fokker G.I Le Faucheur - Нидерланды - 1937
-
Flight 1937-05 / Flight
More commercial Junkers with their economical heavy-oil Jumos.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-12 / J.Stroud - Wings of Peace
Регистрационный номер: D-AREV [3] Another view of D-AREV, the second prototype Ju 86 transport, which first flew in May 1935. The smoke from the Diesels was typical.
-
Flight 1937-02 / Flight
Looking, with its flaps down, less handsome than it actually is - the ten-passenger Ju.86, which has Jumo compression-ignition engines. D.L.H. now have a number in service.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-01 / ??? - The airliner that went to war
The production Ju 86B-0 with Jumo engines.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-12 / J.Stroud - Wings of Peace
Регистрационный номер: D-AKOI, D-AQER Lufthansa's Ju 86B-0 D-AQER Jnselsberg at Hamburg. Beyond is the C-1 D-AKOI Kaiserstuhl. The nose of the Ju 160 D-UBIQ Silberfuchs can be seen on the right.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Junkers Ju.60 / Ju.160 - Германия - 1932
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-12 / J.Stroud - Wings of Peace
Регистрационный номер: D-AREV [3], D-AZAH A pair of Junkers Ju.86s (one with Jumo diesels) paraded at Tempelhof with a Heinkel He.70 and an early Junkers used for testing the original Jumo. A Ju.52 peeps in at the top corner.
This Tempelhof line-up in 1936 shows the production prototype Ju 86 D-AREV with straight-tapered wing, D-AZAH Feldberg the B-0 c/n 0012, Heinkel He 70G-1 D-UMIM Albatros, and Junkers-F 24 D-UDOP.Другие самолёты на фотографии: Heinkel He-70/Не-170 Blitz - Германия - 1932Junkers G 23 / G 24 - Германия - 1924Junkers Ju.52/3m - Германия - 1931
-
Flight 1937-03 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: D-AKOP [2] A general view of the assembled machines at Almaza. Note the big Junkers Ju.86.
-
Мировая Авиация 113
Регистрационный номер: D-AKOP [2] Насколько элегантно выглядели лайнеры Ju 86, настолько же уродливо смотрелись бомбардировщики и высотные разведчики Люфтваффе. На снимке предсерийный самолет, получивший имя "Kismet", ставший в 1937 году победителем 3-х авиационных состязаний аэроклуба Каира.
A Triton among the minnows: the Junkers Ju.86 (two 510/600 h.p. Jumo diesels) which took first place in the Circuit of the Oases - the general efficiency competition. -
Flight 1935-10 / Flight
THE NEWEST JUNKERS: Well-tried Junkers features are retained in the Ju. 86, a ten-passenger twin-engined high-speed machine which will be put into service by D.L.H. next year. The stressed skin is, however, smooth in this machine, which has a maximum speed of 225 m.p.h.
-
Flight 1936-05 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: HB-IXI [4] ALPINE FREIGHTER: The latest addition lo Swissair's fleet - a Junkers Ju 86 fitted with two Jumo 205 diesel engines. This machine will be used primarily as a mail and freight carrier.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-12 / J.Stroud - Wings of Peace
Регистрационный номер: HB-IXI [4] The first export Ju 86, Swissair’s Ju 86B-0 HB-IXI. It was delivered in April 1936 and may have been the first of the type to enter airline service.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-01 / ??? - The airliner that went to war
Регистрационный номер: HB-IXI [4] The first Ju 86B-0 supplied to Swissair: it operated for only a few month.
-
Air Enthusiast 1998-09 / J.Grant - Corrugated Masterpieces
Регистрационный номер: VH-UYA [2] Ju 86 montage on Junkers advertising literature.
-
Air Enthusiast 1998-09 / J.Grant - Corrugated Masterpieces
Регистрационный номер: VH-UYA [2] Australia’s sole Ju 86, VH-UYA, at an RAAF station soon after its arrival from Brisbane.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-12 / J.Stroud - Wings of Peace
Регистрационный номер: ZS-AGF [2], ZS-AGG [2] ZS-AGF and ZS-AGG, the second and third South African Airways Ju 86s, were originally fitted with Rolls-Royce Kestrel engines. They have B-series fuselages. A total of 18 Ju 86s was ordered by the airline - the biggest civil order for the type. In 1939 they were taken over by the South African Air Force, armed and used on maritime patrol, escort and reconnaissance duties until 1942.
-
Flight 1937-06 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: ZS-AGF [2], ZS-AGG [2] CIVIL KESTRELS: These two South African Airways' Junkers Ju.86s, seen flying near Dessau, are fitted with fully supercharged Kestrel XVIs, and should by now have reached Johannesburg on their delivery flight
ZS-AGG - one of the original Ju 86s for South African Airways, with Rolls-Royce Kestrel engines. Before delivery, Pratt & Whitney Hornet engines were substituted, bringing the aircraft up to Ju 86Z-7 standard. -
Flight 1940-02 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: ZS-AGJ A Junkers Ju.86 belonging to South African Airways. These machines can be converted into bombers.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-01 / ??? - The airliner that went to war
Регистрационный номер: ZS-ANF A SAA Ju 86Z-7, temporarily named Saul Solomon before becoming Jan van Riebeeck.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-01 / ??? - The airliner that went to war
Среди зарубежных покупателей Ju 86 была и Южная Африка. Доработанные бомбардировщики Ju 86Z-7 из 12-й эскадрильи SAAF (на снимке) первоначально использовались авиакомпанией "South African Airways" для коммерческих перевозок. Эти самолеты были оснащены рядными двигателями Pratt & Whitney Hornet.
Junkers Ju 86Z-7s of the South African Air Force, after conversion from transports to bomber configuration. -
Air Enthusiast 1972-01 / ??? - The airliner that went to war
On of the SAA Junkers after conversion for the South African Air Force.
-
Flight 1940-10 / Flight
Thereby hangs a tale: The result of a raid by the South African Air Force on an Italian aerodrome in Abyssinia. It is apparent from the tail which appears in the top left corner that the machines used by the S.A.A.F. were Junkers Ju 86s bought before the outbreak of hostilities.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-12 / J.Stroud - Wings of Peace
Регистрационный номер: M-215 M-215, one of the BMW-engined Ju 86Z-2s supplied to Manchuria. This aeroplane had a C-series fuselage.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-01 / ??? - The airliner that went to war
Регистрационный номер: M-223 One of several Ju 86Z-2s supplied to Manchuria for operation by the local airline, which was closely controlled by the military authorities. These aircraft carried military-style insignia on the wings and tail unit, and the "registrations" fell between M-212 and M-223.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-12 / J.Stroud - Wings of Peace
Lloyd Aereo Boliviano's Ju 86Z-7 Illimani.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1938 / 03 - All the world's aeroplanes
Регистрационный номер: SE-BAE [3] The Junkers Ju.86 Commercial Monoplane (two 715 h.p. Pratt & Whitney "Hornet" engines).
The sole Ju 86Z-7 supplied to Sweden, for operation as a mail carrier and therefore without fuselage windows. -
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-12 / J.Stroud - Wings of Peace
Регистрационный номер: SE-BAE [3] Swedish Air Lines' Ju 86Z-7 mail carrier SE-BAE Svalan. This has the wedge-like tail extension.
-
Aviation Historian 8
Регистрационный номер: SE-BAE [3] Jan Forsgren sent TAH this rare photograph of Junkers Ju 86Z-7/Tp 9 SE-BAE
-
Flight 1938-09 / Flight
Junkers Ju.86 bombers of the Swedish Air Force stage a fly-past.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-01 / ??? - The airliner that went to war
The same aircraft modified for service with the Swedish Air Force.
-
Aviation Historian 6 / B.Lindwall - Mosquito vs Bull: Fliying the J 30 in Flygvapnet service
Three J 30s alongside a Flygvapnet Junkers Ju 86K (designated B 3 in Swedish service). Three B 3Ds were converted to serve as radar operator trainers in 1949, one of which was fitted with the complete nose section of written-off Mosquito s/n 30006.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: De Havilland Mosquito F - Великобритания - 1941
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-12 / J.Stroud - Wings of Peace
Ju 86 production line at the Junkers Flugzeug-und-Motorenwerke AG at Dessau, Germany.
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-01 / ??? - The airliner that went to war
Junkers Ju 86s in production for South African Airways in 1936.
-
АвиаМастер 2003-07 / Р.Ларинцев, А.Заблотский - Партизанское небо II: взгляд с другой стороны /Неизвестные страницы истории/
"Юнкерс" Ju 86G-1, принадлежавший одной из немецких Blindflugschule (школ слепых полетов). Возможно, именно эту машину сбили советские партизаны 30 сентября 1943г.
-
Flight 1940-02 / Flight
A modified version of the Junkers Ju 86K bomber has a cleaned-up nose in comparison with the older type.
-
Мировая Авиация 96
На снимке, сделанном в Бернбурге, вероятно изображен четвертый серийный Ju 88A-1, без оборонительного вооружения. На заднем плане виден Ju 86G.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Junkers Ju.88 - Германия - 1936
-
Flight 1937-10 / Flight
Регистрационный номер: D-ADAA The projection of so much rear armament on the Junkers Ju. 86K bomber is deplorable aesthetically and aerodynamically. The "dustbin" would be more at home in a museum than on such a fine bombing machine.
-
Моделист-Конструктор Бомбардировщики Второй мировой войны
Ju 86E-2, использовавшийся как учебный
-
Aviation Historian 40 / R.Forsyth, A.Dillmann - Eyes of the Luftwaffe (1)
Another type on strength with the FFS C flying schools was the twin-engined Junkers Ju 86, which had initially seen use as a prewar airliner on Deutsche Luft Hansa’s Blitzstrecken (“lightning stretch”, i.e. high-speed) routes, but which was also adapted into a bomber for the fledgling Luftwaffe. This Ju 86E-1 is seen in the colours of Kampfgeschwader 253.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1938 / 03 - All the world's aeroplanes
The Junkers Ju.86K Twin-engined Bomber Monoplane (two Junkers "Jumo 205" heavy-oil engines).
-
Моделист-Конструктор Бомбардировщики Второй мировой войны
Ju 86D-1 в полете
-
Aviation Historian 25 / G.Baughen - The case for appeasement?
The first prototype of the Junkers Ju 86 made its maiden flight on November 4, 1934, and was unusual in that the type was designed from the outset to be powered by a pair of 600 h.p. Junkers Jumo 205 diesel engines, as seen fitted to these Ju 86Ds of 4./KG 253. Other variants of the Ju 86 were fitted with BMW 132 radial engines.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1938 / 02 - The progress of the world in military aviation during the year 1937-38
A Flight of Junkers Ju.86K Bombers (Junkers "Jumo 205" Diesel engines) of the Deutsche Luftwaffe.
-
Flight 1937-11 / Flight
DIESEL-POWERED BOMBERS: Junkers Ju.86 bombers of the German Air Force. These machines are essentially similar to the civil "86" and are fitted with a pair of Junkers Jumo 205 diesel engines of 510/600 h.p. A peculiar retractable "dustbin" turret below the fuselage is a characteristic feature.
-
Flight 1938-05 / Flight
The Junkers Ju.86K bomber with twin Junkers Jumo engines. Machines of this type equip a number of German squadrons.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1938 / 02 - The progress of the world in military aviation during the year 1937-38
Junkers Ju.86K Bombers of the German Air Force.
-
Авиация и Время 1999-01 / А.Котлобовский, М.Жирохов - Маленькие ВВС в большой войне. ВВС Словакии в 1939 году /Аэроархив/ (1)
Бомбардировщики Ju 86K-2 ВВС Венгрии приближаются к аэродрому Спишска Нова Вес
-
Air Enthusiast 1971-09 / J.Rajninek, J.Sanders - Conflict over the Carpathians
A Ju 86K-2 (actually belonging to the 3/1 "Istennyila" bomber squadron) and He 170As of the Royal Hungarian Air Force. The latter, belonging to the 1st Independent Long-range Reconnaisance Group, flew sorties during the Slovakian-Hungarian fighting.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Heinkel He-70/Не-170 Blitz - Германия - 1932
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1938 / 02 - The progress of the world in military aviation during the year 1937-38
A line of Junkers Ju.86K ("Mercury" engines) Bombers of the Swedish Air Force.
-
Aviation Historian 24 / L.Andersson - Sweden's ghost rocket
The aircraft used for SIGINT/ELINT missions in 1946 was B 3A (Ju 86K-4) serial 150, named Blondie, powered by a pair of 820 h.p. Nohab My III (licence-built Bristol Pegasus III) radial engines. The cylindrical excrescence on the underside of the fuselage just aft of the mainwheels is the radome for its crucial AN/APS-15 navigation radar.
-
Aviation Historian 30 / J.Forsgren - Nattjakt!
With the “clamshell” canopy and revised tail arrangement, this J 33, coded “E”, awaits its next sortie in Sweden. Flygvapnet’s sole nightfighter Wing, F1 had three squadrons, which were the only units to operate the type. Note the pair of North American Sk 16s and a Junkers B 3, as used to train J 33 navigators, in the background.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: De Havilland Venom / D.H.112 - Великобритания - 1949North American T-6 Texan / AT-6 Harvard - США - 1935
-
Aviation Historian 24 / L.Andersson - Sweden's ghost rocket
Blondie was originally on strength with F 11 Wing at Nykoping, but was later transferred to F 1 Wing at Vasteras before moving again to F 8 Wing at Barkarby, near Stockholm. The aircraft wore minimal markings, bearing only its name on the forward fuselage beneath the cockpit and a standard Flygvapnet roundel either side of the rear fuselage. It was later given the fin code number “50”, when based at Bromma.
-
Aviation Historian 24 / L.Andersson - Sweden's ghost rocket
A poor-quality but extremely rare photograph of Blondie’s crew in 1946, with the B 3A in the background. From left to right: Stig Lindberg, pilot; Ulf Mide, observer; Sven-Uno Palmqvist (radio operator); unknown, and SIGINT/ELINT specialist Sture Risberg.
-
Aviation Historian 24 / L.Andersson - Sweden's ghost rocket
During 1936-58 some 56 Junkers Ju 86Ks saw service with Flygvapnet, which designated the type B 3 (B for Bombflygplan - bomber aircraft), 16 of which were licence-produced by Saab. One example, serial 150, seen here, was used by Sweden’s FOA and FRA agencies to investigate the 1946 spate of “ghost rocket” sightings.
-
Flight 1936-12 / Flight
JUNKERS FOR THE NORTH: A batch of Junkers Ju.86 bombers have been ordered by the Swedish Government. The first machine was recently demonstrated at Bromma, near Stockholm, by Captain Soederberg. It is likely that the production machines will be fitted with Swedish-built Pegasus engines, or Mercuries as they are called in Sweden, for some baffling reason.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1980 / Encyclopedia of Aviation - Aircraft A-Z - v4
Swedish Junkers Ju 86.
-
Air Pictorial 1956-09 / Air Pictorial's photo-review
Регистрационный номер: SE-CBO CIVILlANISED Ju 86 seen at Bromma, Sweden, recently (SE-CBO) is an ex-Flygvapnet B3C-2, still retaining "bomber" nose.
-
Jane's All the World Aircraft 1938 / 02 - The progress of the world in military aviation during the year 1937-38
The Delivery of ten Junkers Bombers to the Air Force at Alverca. Two Avro Training Machines are seen in the foreground.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Avro Cadet / Type 631/643 - Великобритания - 1932
-
Flight 1940-03 / Flight
Many of the Continental bombers have vertical bomb stowage. Here is a large projectile is being persuaded into the bomb cell of a Ju 86K.
-
Flight 1939-03 / Flight
A Junkers Jumo 205 Diesel in a Ju.86K.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-12 / J.Stroud - Wings of Peace
The cockpit of a transport Ju 86, showing the asymmetric layout.
-
Flight 1938-02 / Flight Advertisements
Junkers Ju.86 equipped with Askania-Aircraft-Instruments.
-
Мировая Авиация 113
Только 16 Ju 86 достались авиакомпании "Luft Hansa". Часть из них позднее передали Люфтваффе, но несколько самолетов несли службу в DLH до 1945 года. Салон этих машин был относительно просторным и отличался комфортабельными сиденьями.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-12 / J.Stroud - Wings of Peace
The Ju 86’s ten-seat passenger layout.
-
Air Pictorial 1977-03 / J.Rawlings - Kit News
Continuing their (welcome) policy of introducing the Italian Italaeri kits into Britain, Revell (GB) Ltd. recently supplied samples of the two latest aircraft models in the Revell/ltalaeri range, both to 1/72nd-scale. Photo: The Junkers Ju 86, shown here with the type’s original Jumo diesel in-line engines (radials are in the new kit) and in Luftwaffe markings. Outline is good and assembly time-consuming rather than difficult - an excellent representation.
-
Aeroplane Monthly 1988-12 / J.Stroud - Wings of Peace
Регистрационный номер: HB-IXI [4] KEITH WOODCOCK'S painting shows Swissair's Junkers-Ju 86B-0 HB-IXI in the airline's original Ju 86 paint scheme.
-
Flight 1939-09 / Flight
JUNKERS JU 86K. Powered with Junkers Jumo diesels (as shown) or B.M.W. radials, this machine is now regarded as obsolescent. Its performance is inferior to that of the Heinkels and Dorniers though Junkers have lately been producing Ju 88 bombers which are said to be very fast indeed.
-
Flight 1938-04 / Flight
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Bloch MB.160 Languedoc - Франция - 1937Boeing Boeing 314 Clipper - США - 1938Consolidated PBY Catalina - США - 1935Dewoitine D.332 / D.333 / D.338 / D.620 - Франция - 1933Douglas DC-3 / C-47 Skytrain/С-53 Skytrooper / Dakota - США - 1935Douglas DF - США - 1936Focke-Wulf FW.200 Condor - Германия - 1937Latecoere Late 631 - Франция - 1942Liore et Olivier LeO H.246 - Франция - 1937Lockheed Super Electra 14 - США - 1937Martin Russian Clipper / Type 156 - США - 1937Potez Potez 661 - Франция - 1937Potez-CAMS Potez-CAMS 160 / 161 - Франция - 1938Savoia-Marchetti / SIAI SM.83 - Италия - 1937Sikorsky S-43 Baby Clipper/JRS/Y1OA-8 - США - 1936Sud-Est SE.200 - Франция - 1943
-
Flight 1940-12 / Flight
Comparative pictures by "J.P." of ten twin tails, all from the same angle: The twin arrangement of fins and rudders has advantages from both aerodynamical and military aspects. It gives the rear gunner an excellent field of fire, especially if the turret is placed fairly far aft. Smaller control areas can be used and, since these surfaces are in the airscrew slipstream, good control is obtained at low speeds.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Armstrong Whitworth Whitley / A.W.38 - Великобритания - 1936Blohm und Voss Ha.139 - Германия - 1936Breda Ba.88 Lince - Италия - 1936De Havilland Flamingo / D.H.95 - Великобритания - 1938Dornier Do.17Z / Do.215 - Германия - 1939FIAT BR.20 Cicogna - Италия - 1936Handley Page Hampden / H.P.52 - Великобритания - 1936Lockheed Hudson A-28 / A-29 - США - 1938Messerschmitt Bf.110 - Германия - 1936
-
Flight 1937-05 / Flight
Four German types in regular service fitted with Junkers Jumo compression-ignition engines.
Другие самолёты на фотографии: Dornier Do.18 - Германия - 1935Junkers G 38 - Германия - 1929Junkers Ju.52/3m - Германия - 1931
-
Air Enthusiast 1972-01 / ??? - The airliner that went to war
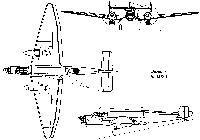
The head-on, plan and centre side-view depict the Ju 86C-1, with Jumo 205 engines and rear-fuselage fairing. The upper side-view shows the version with Kestrel engines and without the fairing while the lower side-view depicts the Ju 86Z-7.
-
Моделист-Конструктор Бомбардировщики Второй мировой войны
Junkers Ju 86D-1
- Фотографии